Figure 1.
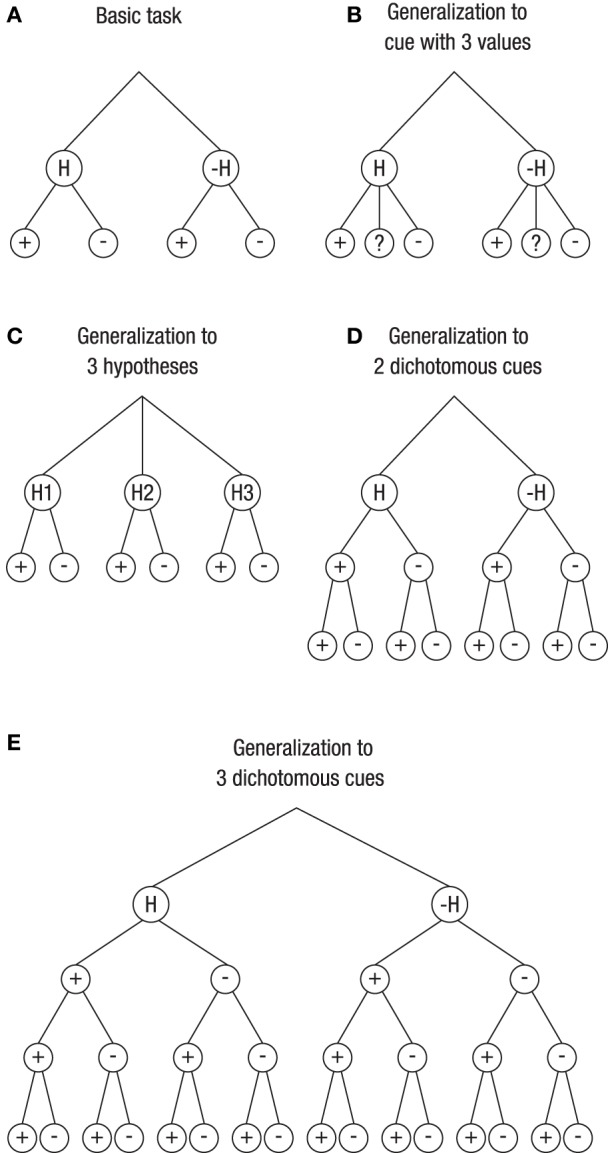
Generalization of the basic Bayesian inference task (with two hypotheses and one dichotomous cue; A) to more complex tasks (B–E). The layers below the hypotheses depict the cue values (or data). Unknown cue values are denoted as “?” (B). For a pair of two hypotheses (one being the complement of the other), these are denoted as H and –H (A,B,D,E), and for a triple of hypotheses, they are denoted as H1, H2, and H3 (C).
