Figure 1.
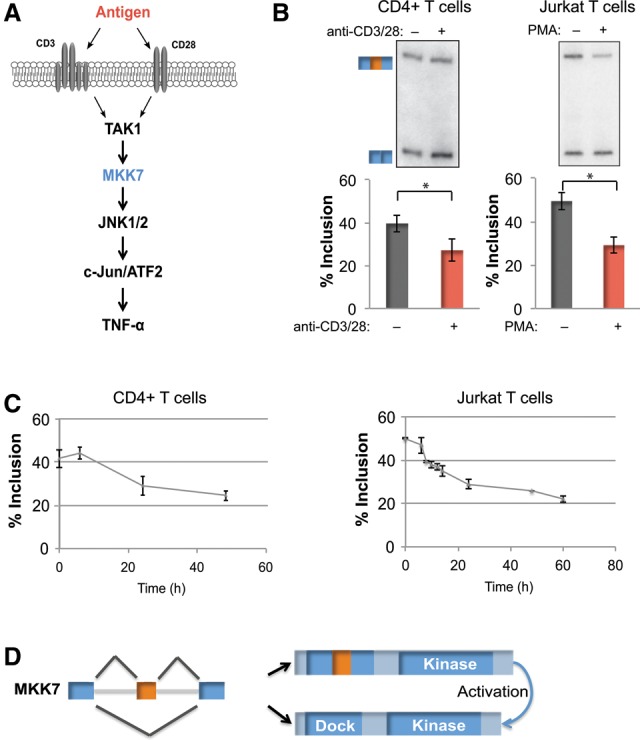
MKK7 is alternatively spliced in response to activation of primary human CD4+ T cells and a model Jurkat T-cell line. (A) Schematic of JNK pathway activation in the context of TCR signaling. (B, left panel) Representative RT–PCR gel and quantification of MKK7 exon 2 (MKK7-E2) inclusion in unstimulated and activated (anti-CD3/CD28, 48 h) primary human CD4+ T cells. n = 9. (Right panel) Representative RT–PCR gel and quantification of MKK7-E2 inclusion in unstimulated and activated (PMA, 48 h) Jurkat T cells. n = 14. In all of the figures, error bars represent standard deviation. (C) Time course of average MKK7-E2 inclusion in response to activation in primary human CD4+ T cells (anti-CD3/CD28) (left) or Jurkat T cells (PMA) (right) as quantified by RT–PCR. n = 3. (D) MKK7 domain schematic displaying the predicted outcome of MKK7-E2 inclusion on its MAPK-docking site. (*) P < 0.005, Student's t-test. See also Supplemental Figure S1.
