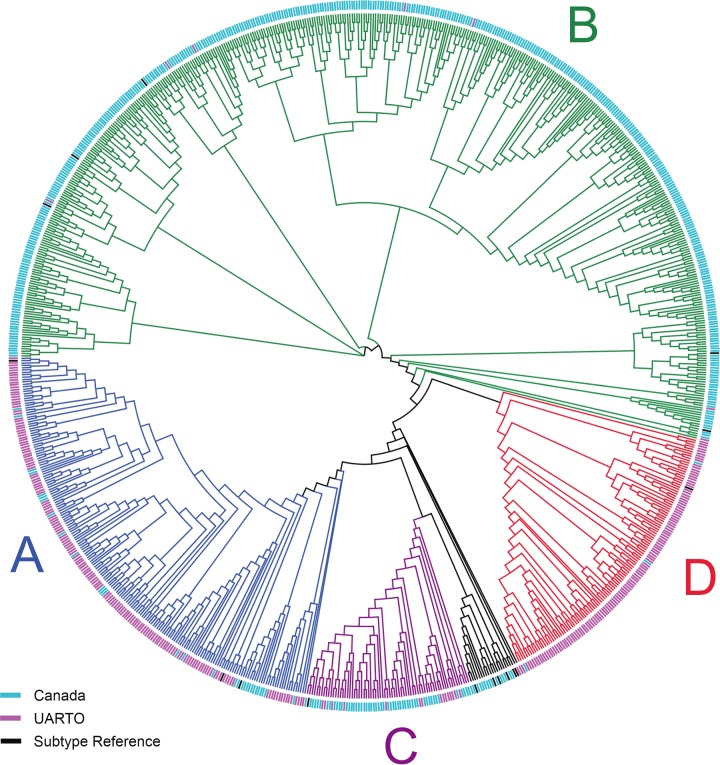
FIG 4.
Phylogenetic tree of samples successfully sequenced by MiSeq sequencing. A neighbor-joining tree constructed from MiSeq consensus sequences (n = 892 clinical samples) is depicted as a cladogram (with unscaled branch lengths). Mixed bases were called when minority bases exceeded 20% prevalence. Samples with <100-fold coverage were excluded. Sequences clustered by cohort and HIV subtype in agreement with expected prevalence rates. HIV-1 subtype consensus sequences (n = 16) (black tip labels) spanning RT codons 90 to 234 were included and represent subtypes A1, A2, B, C, D, F1, F2, G, and H, as well as recombinant viruses AE, AG, AB, BC, CD, BF, and BG (retrieved from http://www.hiv.lanl.gov). Canadian HIV RT sequences (blue tip labels) were primarily subtypes B and C, and UARTO HIV RT sequences (purple tip labels) were primarily subtypes D and A.