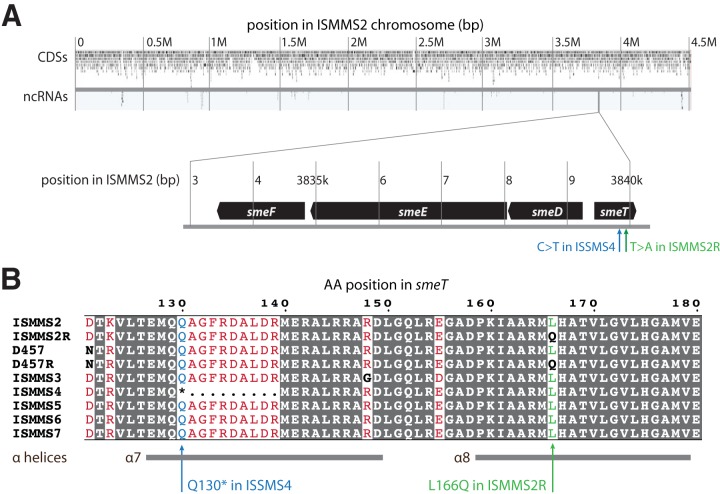
FIG 1.
Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) observed in quinolone-resistant S. maltophilia clinical isolates. (A) Assembled circular chromosome for ISMMS2, including predicted coding domain sequence (CDS) and noncoding RNA (ncRNA) features drawn with ChromoZoom (23). Horizontal position corresponds to base pair location. The smeDEF operon is shown in the detail callout, which highlights both the smeT c.497T>A SNV that emerged in ISMMS2R and the aligned location of the smeT c.388C>T SNV (resulting in a premature stop codon) in ISMMS4. ISMMS2 and ISMMS2R are serial isolates from a single patient before and after development of quinolone resistance, while ISMMS4 was quinolone resistant at initial isolation from a different patient. (B) Multiple-sequence alignment of part of the predicted smeT product in each of the clinical isolates, the D457 reference assembly, and its quinolone-resistant counterpart D457R. Predicted α-helices (13) are depicted as gray bars below the sequence. Positions identical in all sequences are shaded with a dark gray background, equivalent substitutions are in red, and nonequivalent substitutions are in black and boldface. The L166Q and Q130* (*, stop codon) polymorphisms are highlighted.