Figure 7.
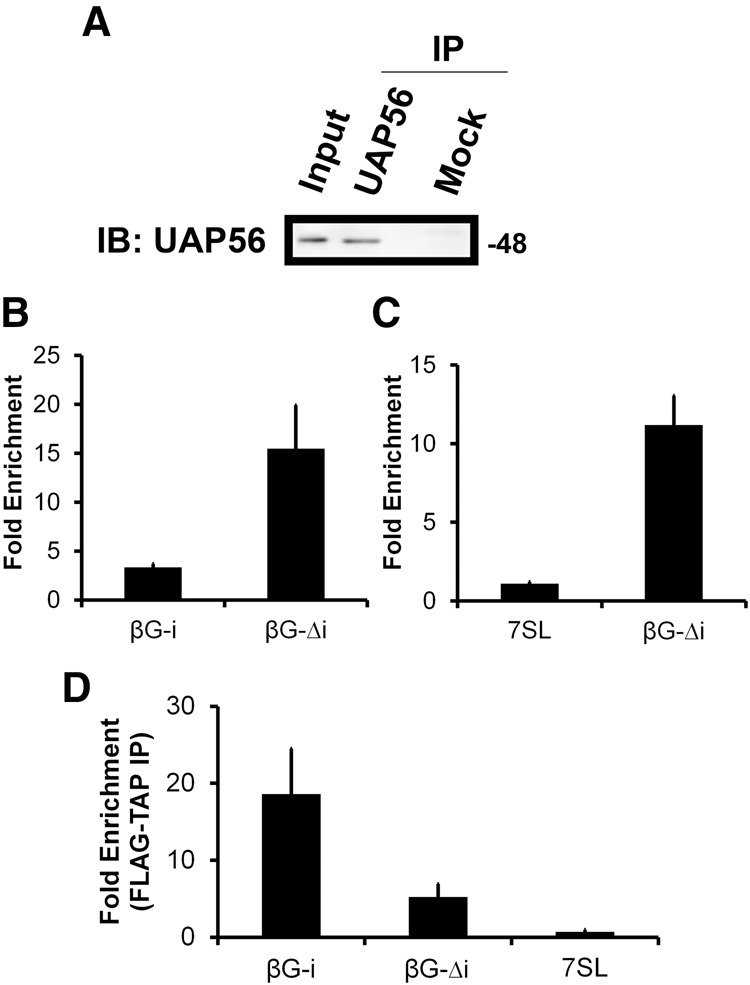
Strong UAP56-association and weak TAP-association with βG-Δi mRNA in vivo. (A) UAP56 was immunoprecipitated from U2OS lysates using rat anti-UAP56 antibodies prebound to protein G sepharose. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting for UAP56. Rat preimmune serum was used in the mock immunoprecipitation reaction. (B,C) U2OS cells were transfected with plasmids containing βG-Δi (B,C) or βG-i (B). After 14–18 h, cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitated with rat anti-UAP56 antibodies or rat preimmune serum. RNA was collected from fractions and converted to cDNA using βG-specific primers (B) or random hexamers (C). The fold enrichment of mRNAs in anti-UAP56 over preimmune precipitates was quantified by RT-qPCR. Each bar represents the average and standard error of three independent experiments. (D) U2OS cells were cotransfected with plasmids containing FLAG-TAP and either βG-Δi or βG-i. After 14–18 h, cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitated with beads conjugated to anti-FLAG antibodies or protein A. RNA was collected from fractions and converted to cDNA using random hexamers. The fold enrichment of mRNAs in the FLAG precipitates over protein A precipitates was quantified by RT-qPCR. Each bar represents the average and standard deviation of two independent experiments.
