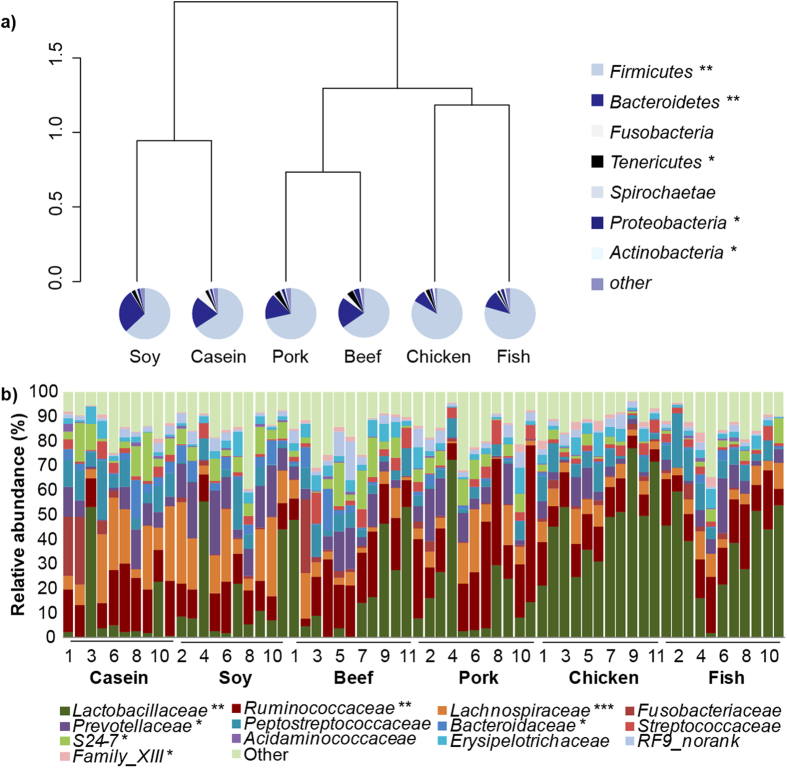
Figure 3. The composition of gut bacteria in caecum at the phylum and family levels.
Relative abundance of the different phyla in response to different dietary proteins (average percentage). Bray-Curtis similarity clustering analysis of caecal bacteria at the phylum level showed that six groups can be clustered into three classes: white meat protein class (chicken and fish protein groups), red meat protein class (beef and pork protein groups) and non-meat protein class (casein and soy protein group). Taxon-based analysis at the family level. Each column represents one animal. Note: The numbers of animals for beef, casein, chicken, fish, pork and soy protein groups are 11, 10, 11, 11, 11 and 10 respectively. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and means were compared by Duncan’s multiple comparison.