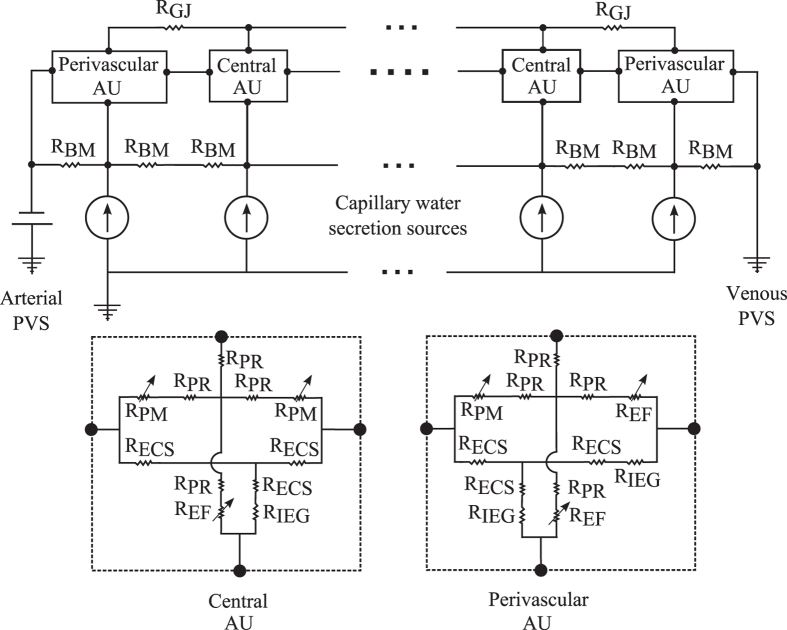
Figure 2. Electrical analogue model of cerebral water transport between arterial and venous paravascular spaces (PVS).
Definitions of the abbreviations referring to the physical model domain are given in Fig. 1. The voltage source represents the driving pressure difference between arterial and venous paravascular spaces that are connected by resistances (R) representing the resistance to fluid flow of capillary basement membrane (BM) segments and astrocyte units (AU). Each astrocyte unit (AU) includes resistances of both intracellular (cell processes, PR) and extracellular (ECS) pathways which are linked by membrane resistances, namely those of the astrocyte endfoot membrane (EF) and the remainder of the astrocyte plasma membrane (PM). Since these membrane resistances are dependent on the AQP4 expression level, they are indicated as variable resistances (arrows). Gap junction (GJ) resistances connect the intracellular spaces of two neighbouring astrocytes.