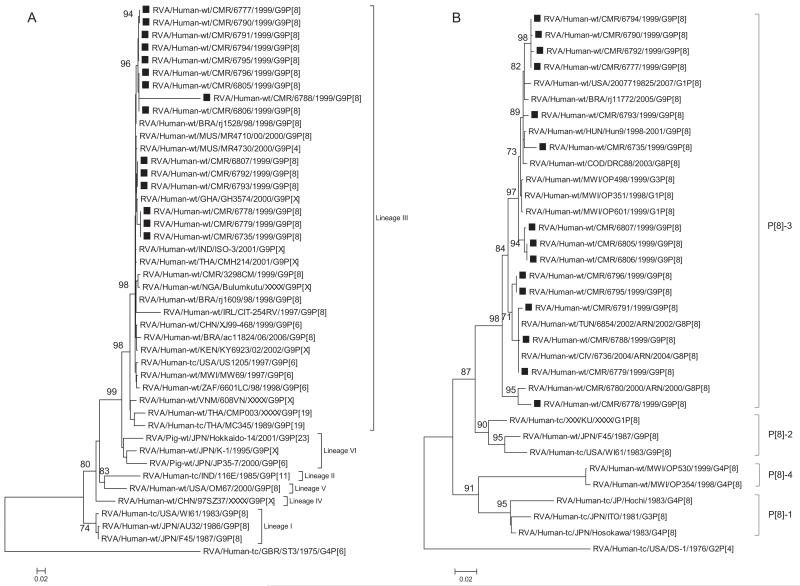
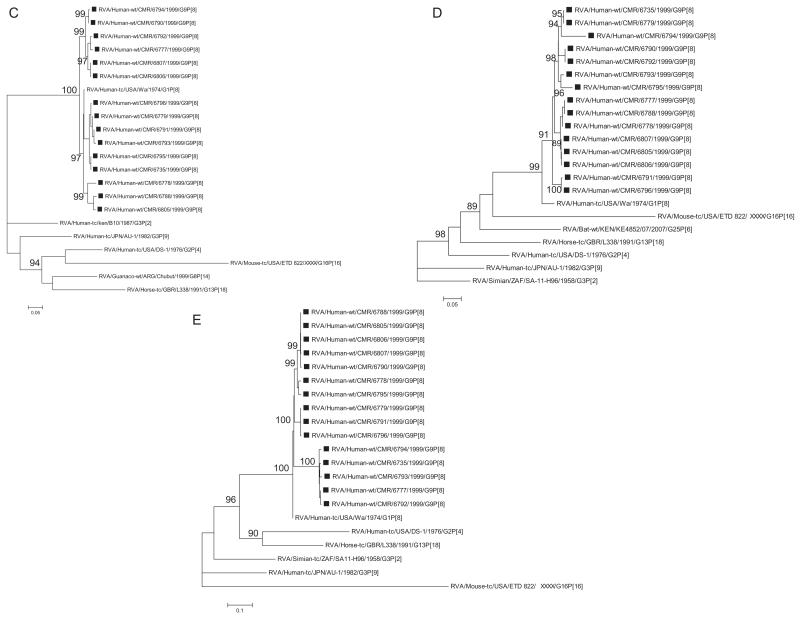
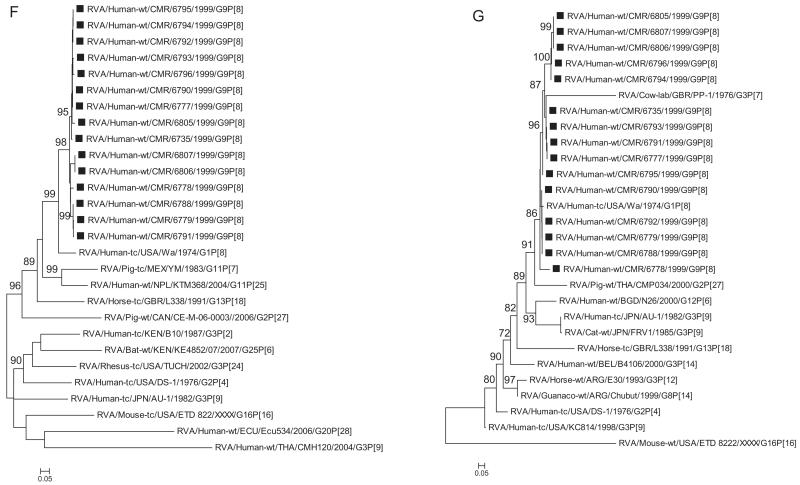
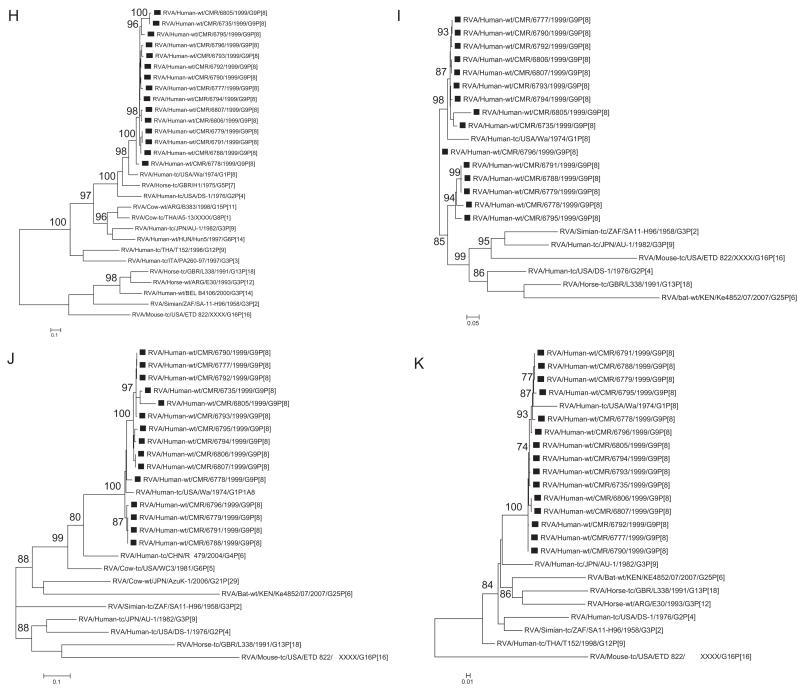
Fig. 1.
A–K Maximum likelihood phylogenetic trees built in PhyML with aLRT statistics as support show the genetic relationships of nucleotide sequences of VP7 (A), VP4 (B), VP1(C), VP2 (D), VP3 (E), VP6 (F), NSP4 (G), NSP1 (H), NSP2 (I), NSP3 (J) and NSP5 (K) of human G9P[8] rotaviruses from Cameroon with known human and animal rotavirus strains from GenBank database. The trees were drawn to scale. Only aLRT values of 70% and greater are shown. The strains labeled with filled squares indicate the Cameroon G9P[8] isolates sequenced in this study. The scale bar at the bottom of the trees indicates genetic distance.