Figure 3.
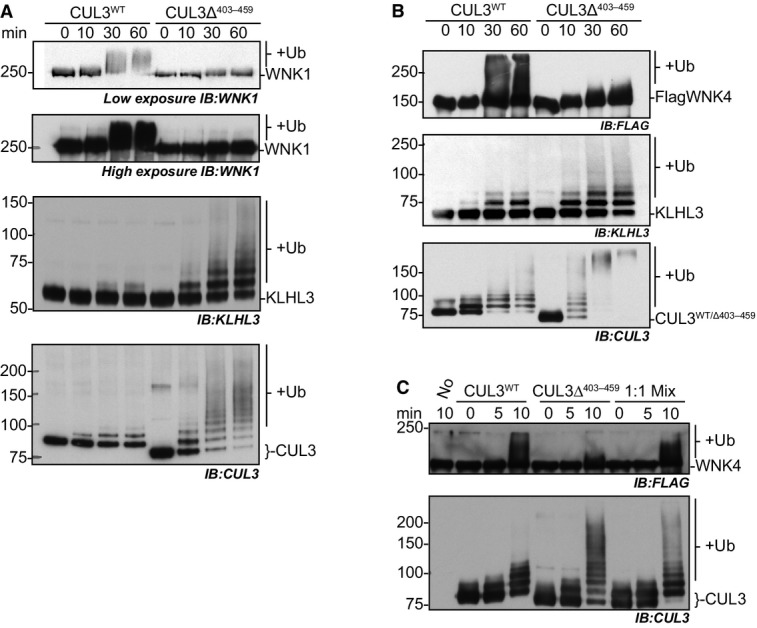
CUL3Δ403–459 is unable to ubiquitylate WNK1 or WNK4 kinases in an in vitro system, and this deficiency cannot be rescued by the presence of CUL3WT
- A–C In vitro ubiquitylation assays were performed as described in Figure 2, but with the addition of immunoprecipitated WNK1 in (A), or immunoprecipitated over-expressed FLAG-WNK4 in (B, C) (see Materials and Methods). The WNK kinases are modified by CUL3WT-KLHL3, with the higher molecular weight smear observed in anti-WNK1 and anti-FLAG panels representative of multiple ubiquitin molecules being covalently attached to the WNK protein. CUL3Δ403–459 is unable to modify WNKs. Samples from the same assay reactions were divided to allow immunodetection of the different protein components modified within the same assay reaction. (C) CUL3WT, CUL3Δ403–459 and an equimolar solution CUL3WT:CUL3Δ403–459 (1:1 Mix) were incubated with KLHL3 and immunoprecipitated FLAG-WNK4 in ubiquitylation reactions to determine the influence of CUL3Δ403–459 on the ubiquitylation activity of CUL3WT. Notably, the presence of CUL3Δ403–459 does not inhibit WNK ubiquitylation by CUL3WT.
