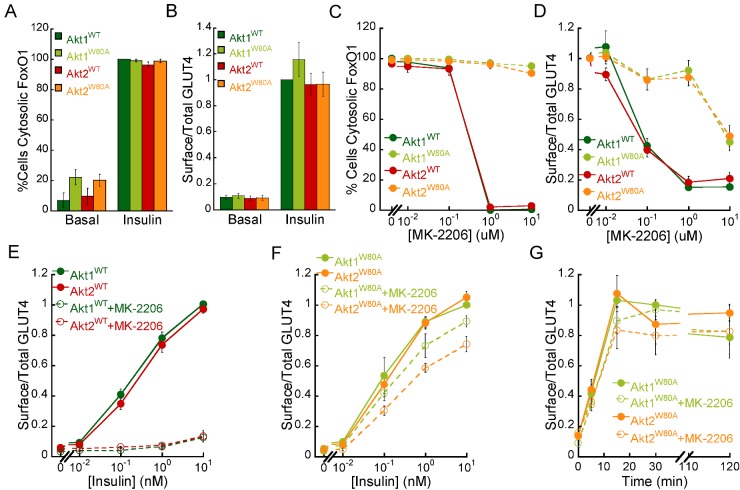
Figure 3. Akt1W80A and Akt2W80A regulate insulin-mediated FoxO1 nuclear exclusion and GLUT4 translocation.
(A) Percentage of cells expressing Akt1WT, Akt1W80A, Akt2WT or Akt2W80A that display cytosolic FoxO1–GFP in basal (starved) and following 1 nM insulin stimulation for 30 min. (B) Surface to total HA–GLUT4–GFP in basal (starved) and 1 nM insulin-stimulated adipocytes expressing Akt1WT, Akt1W80A, Akt2WT and Akt2W80A. For each experiment surface to total GLUT4 values were normalized to that of insulin-treated Akt1WT cells. Dose–response analyses of MK-2206 inhibition of insulin-mediated FoxO1–GFP nuclear exclusion (C) and HA–GLUT4–GFP translocation (D) in adipocytes. Adipocytes expressing WT or W80A Akt mutants were pre-treated with MK-2206 for 1 h as noted followed by stimulation with 1 nM insulin for 30 min. (E) Insulin-dose response analyses of HA–GLUT4–GFP translocation in Akt1WT and Akt2WT adipocytes in the presence or absence of 1 μM MK-2206. For each experiment, surface to total GLUT4 measurements were normalized to that of 10 nM insulin-treated Akt1WT cells. (F), Insulin dose–response analyses of HA–GLUT4–GFP plasma membrane translocation in Akt1W80A and Akt2W80A adipocytes in the presence or absence of 1 μM MK-2206. For each experiment surface to total GLUT4 measurements were normalized to that of 10 nM insulin-treated Akt1W80A cells. (G) Time course analyses of insulin-mediated GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes. Cells were treated with vehicle or 1 μM MK-2206 for 1 h prior to 1 nM insulin stimulation. For each experiment surface to total GLUT4 values were normalized to that of 15 min insulin-treated Akt1W80A cells. All data are the average of at least three independent experiments ± S.E.M.