Fig. 2.
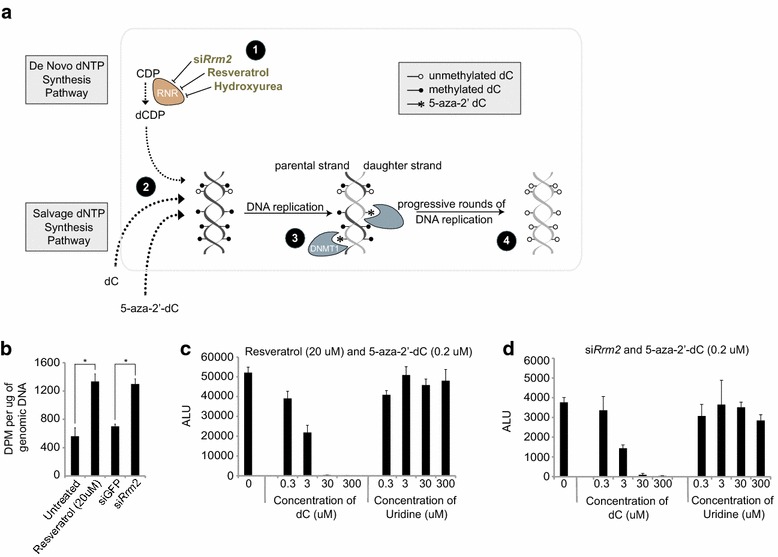
Inhibition of RNR enhances DNA incorporation of 5-aza-2′-dC to elicit XCR. a Illustration of model in which (1) inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) by various means leads to (2) increased relative dCTP utilization for DNA synthesis from salvage pathways which are supplemented with exogenous 5-aza-2′-dC. (3) DNMT1 inhibition occurs upon binding to DNA-incorporated 5-aza-2′-dC leading to (4) increased loss of DNA methylation with successive cell divisions. b Quantification of 3H-5-aza-2′-dC (3H-Decitabine) incorporation into genomic DNA upon either resveratrol treatment or Rrm2 knockdown for 48 h. Genomic DNA was isolated and an equal volume measured for 3H-Decitabine incorporation (disintegrations per minute, DPM), then normalized to the amount of DNA loaded (μg). Error bars indicate standard deviation from three independent treatment wells. Asterisks indicate p < 0.01 by Student’s T-test. c Xi-luciferase reactivation assay as in Fig. 1di in the presence of 0.2 μM 5-aza-2′-dC and 20 μM resveratrol and increasing concentrations of deoxycytidine (dC) or uridine. ALU represents luminescence unit values. d As in c except with siRrm2 in the place of resveratrol
