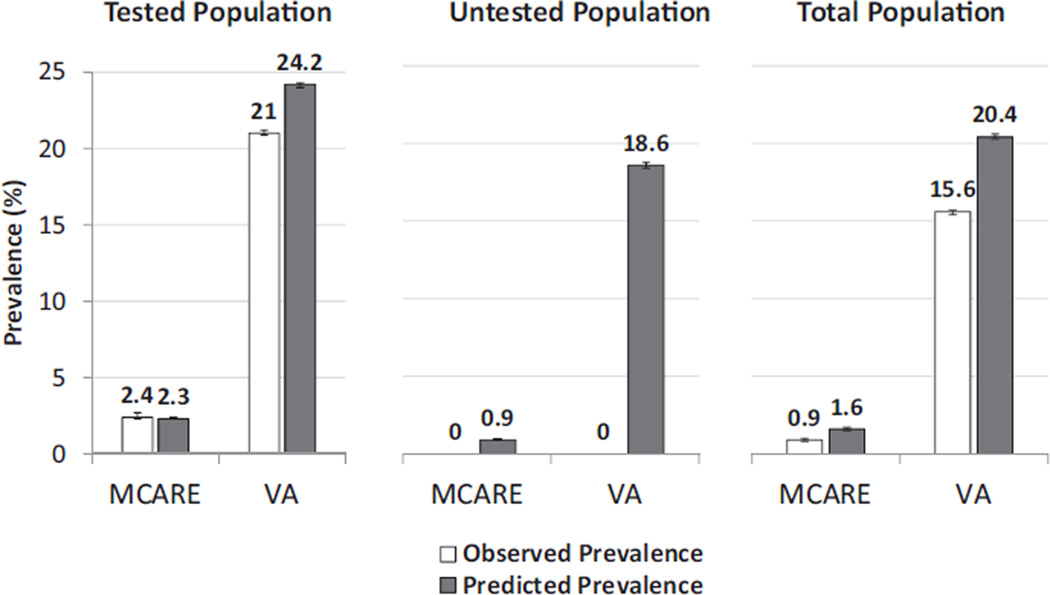
Figure 1.
Observed versus predicted prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 3–5 in the M-CARE and Veterans Affairs (VA) health care systems. Predicted prevalence was derived from a logistic regression model fitted using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005–2006 data set to predict the presence of CKD stages 3–5 based on age, race (non-Hispanic black vs nonblack), diabetes mellitus, hypertension, anemia, and sex. The coefficients from this model were used to produce estimates of the prevalence of CKD within the VA and M-CARE cohorts based on the respective characteristics of those populations. Observed and predicted prevalence are shown for both the population tested for serum creatinine (Tested Population) and those not tested (Untested Population). The predicted prevalence presented for the total population is a combination of the observed prevalence in the tested population and the prevalence in the untested population based on the NHANES model. The vertical thin bars represent 95% confidence intervals.