Figure 6.
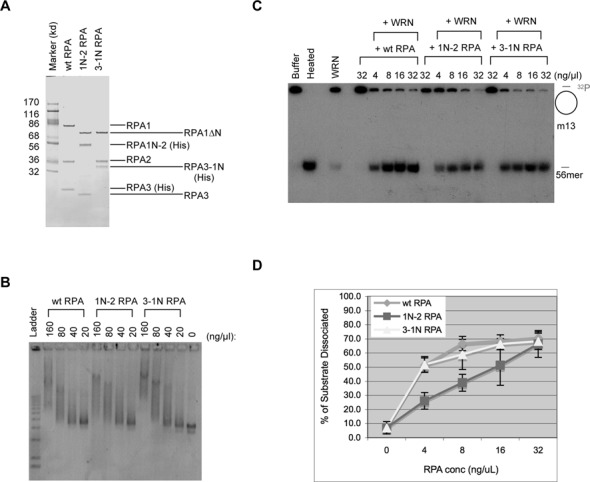
The spatial location of RPA1N affects the stimulation of WRN's helicase activity. (A) A gel showing recombinant Xenopus wild-type RPA and two mutant RPAs. Proteins were separated by a 4–12% NUPAGE MES gel (Invitrogen, CA, USA) and stained by Coomassie brilliant blue. (B) An agarose gel showing the binding activity of the wild-type and mutant RPAs to ss-m13 DNA. (C) Effect of wild-type RPA and mutant RPAs on the unwinding activity of WRN. The substrate was a 32P-labeled 56mer oligonucleotide annealed to m13 ss-DNA. (D) Quantitaton of the unwinding activity in the presence of wild-type RPA or mutant RPAs. The percentages of the oligonucleotide dissociated were quantitated and the averages and standard deviations were calculated from three sets of data and plotted.
