Figure 4.
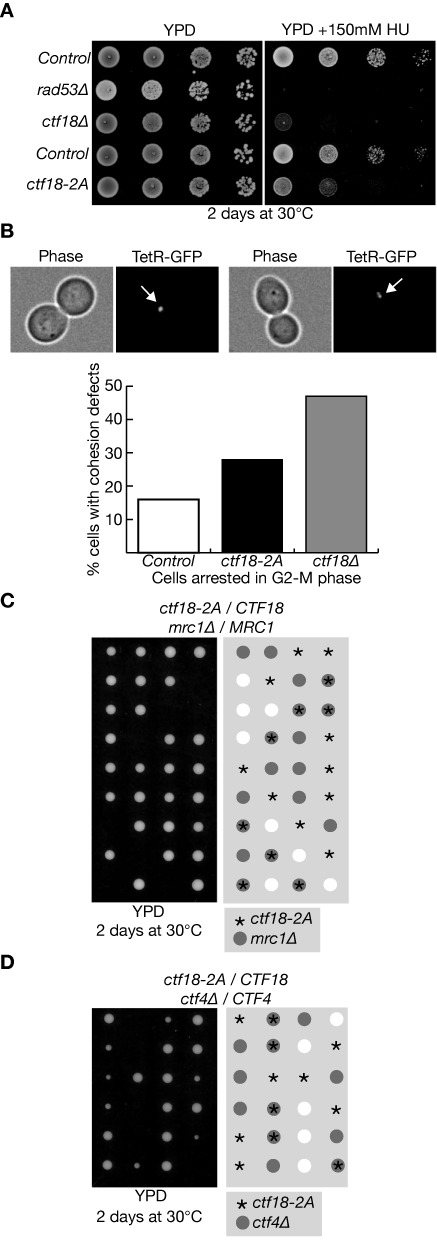
Phenotypes of the ctf18–2A allele. (A) Serial dilutions of control cells (W303–1a), rad53Δ (YAC53), ctf18Δ (YVM164), CTF18::K.l.TRP1 (wild type CTF18 but with the K.l.TRP1 marker inserted into the genomic locus, after the STOP codon of CTF18; YLG316) and ctf18–2A (also with the K.l.TRP1 marker inserted after the STOP codon of CTF18; YLG320) were plated on YPD medium, or YPD supplemented with 150mM hydroxyurea (HU), then grown for 2 days at 30°C. (B) Control cells (CTF18-K.l.TRP1; YLG445), ctf18–2A (ctf18–2A K.l.TRP1; YLG447) and ctf18Δ::K.l.TRP1 (YLG449), all expressing the Tet-repressor fused to GFP and with an array of the Tet-operator sites at the ura3 locus, were grown at 30°C and then arrested in G2-M phase by addition of nocodazole. Defects in sister chromatid cohesion were scored microscopically, by examining 100 cells and determining the percentage with two dots of TetR-GFP instead of one (examples of each class are shown in the upper panels). (C) Diploid cells with the genotype ctf18–2A / CTF18 mrc1Δ / MRC1 (YLG292) were sporulated and then subjected to tetrad analysis on YPD medium. The image was taken after two days growth at 30°C. (D) Tetrad analysis of the meiotic progeny of ctf18–2A / CTF18 ctf4Δ / CTF4 (YLG263).
