Figure 2.
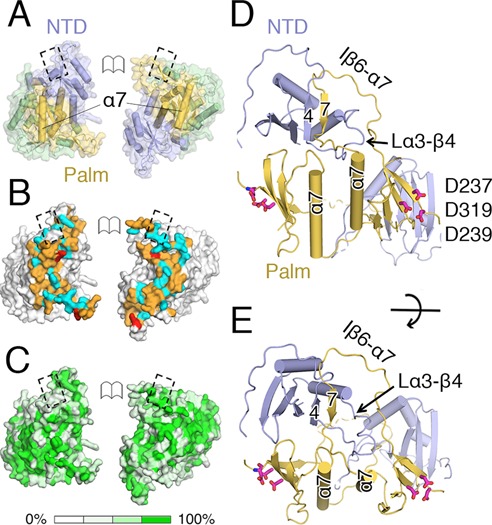
mtPAP dimer. (A) Open-book view of the mtPAP dimer's intermolecular interface; the domains are colored as in Figure 2 and are interacting with each other; the α7 of each monomer is shown. The dashed boxes indicate matching surfaces. (B) View as in (A) with the surfaces colored according to the nature of dimerization contacts. Red: salt-bridging residues; cyan: residues that form putative hydrogen bonds; orange: residues that form van der Waals contacts. (C) Molecular surface of mtPAP oriented as in (A), with the surface shaded according to the degree of conservation among mtPAP family members. The mtPAPs and their dimer-interface residues are typically well conserved. (D and E) Near-orthogonal views highlighting regions involved in the dimerization interface including α7, loop Lα3–β4 and insertion Iβ6–α7. Colors are as in (D): red sticks: catalytic carboxylates.
