Figure 3.
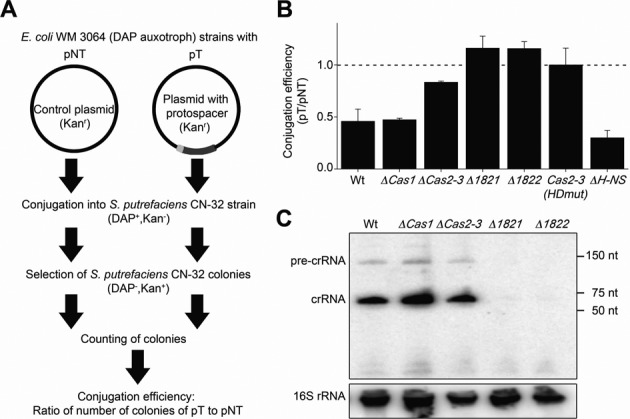
Conjugation assays reveal DNA interference activity of the S. putrefaciens CN-32 CRISPR–Cas system. (A) The experimental set-up of the conjugation assay is depicted. Two plasmids were used: (I) a control plasmid (pNT, plasmid non-target) and (II) a plasmid containing a PAM sequence (light grey) and a sequence matching spacer 13 (dark grey) of the S. putrefaciens CN-32 CRISPR array (pT, plasmid target). The number of S. putrefaciens CN-32 colonies carrying each plasmid was counted and the conjugation efficiency was determined. Interference is observed if pT/pNT is lower than 1 in triplicate assays. (B) The pT/pNT ratio is calculated for conjugation assays into S. putrefaciens CN-32 wild type cells and strains containing deletions of genes encoding Cas1, Cas3, Cas1821, Cas1822 and H-NS. Additionally, a Cas3 active site variant (HDmut, H156A/D157A) was tested. (C) Northern blot analyses were performed with extracted total RNA from S. putrefaciens CN-32 wild-type and cas gene-knockout strains using a 5′-γ-[32P]-ATP labeled probe complementary to the repeat sequence. A stable crRNA pool was absent in the S. putrefaciens CN-32 Δcas1821 and Δcas1822 strains.
