Figure 4.
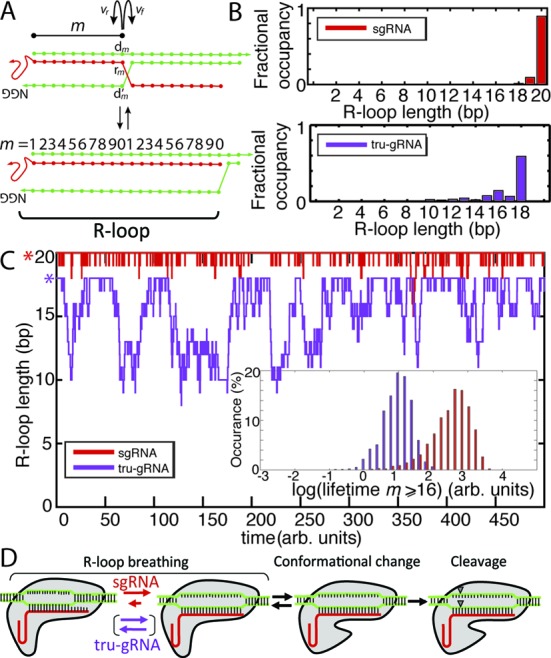
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) experiments reveal differences in the stability of the R-loop, or the structure formed by the protospacer duplex with an invading guide RNA, within stably bound Cas9 for different guide RNA variants. (A) Schematic of strand invasion of the protospacer (green) by the guide RNA (red) for KMC experiments. The R-loop is highlighted. Transition rates for invasion (vf for the rate of m → m + 1, where m is the extent of the strand invasion or, equivalently, the length of the R-loop) or duplex re-annealing (vr for the rate of m → m − 1) are a function of the nearest-neighbour DNA:DNA and RNA:DNA hybridization energies. See text and Supplementary Methods for details. (B) Fractional time that the R-loop is of size m for sg-RNAs (red) or tru-gRNA (purple) derived from KMC experiments ‘at equilibrium’ (simulation initiated at m = 20 or 18, respectively). Simulation run until t ≥ 10 000 (arbitrary units). (C) Kinetic Monte Carlo time course of the R-loop ‘breathing’ for sgRNA (red) and tru-gRNA (purple) after full invasion (simulation initiated at m = 20 or 18, respectively). Asterisks highlight the starting position for the simulation. (inset) Histogram of the respective lifetimes to transit from full invasion to m < the 16th position. (D) Proposed model for the mechanisms governing Cas9/dCas9 specificity, based on results of AFM imaging and KMC experiments (see main text). Cas9/dCas9 binds to the PAM and the guide RNA invades into the PAM-adjacent protospacer duplex. During this strand invasion, the guide RNA must displace the complementary strand of the protospacer. Competition between invasion and re-annealing of the duplex results in a dynamic (‘breathing’) R-loop structure. The stability of the 14th–17th sites of the protospacer-guide RNA interaction, which is dramatically increased by binding at the 19th and 20th sites, promotes a conformational change in the Cas9/dCas9 that authorizes DNA cleavage in Cas9.
