Figure 2.
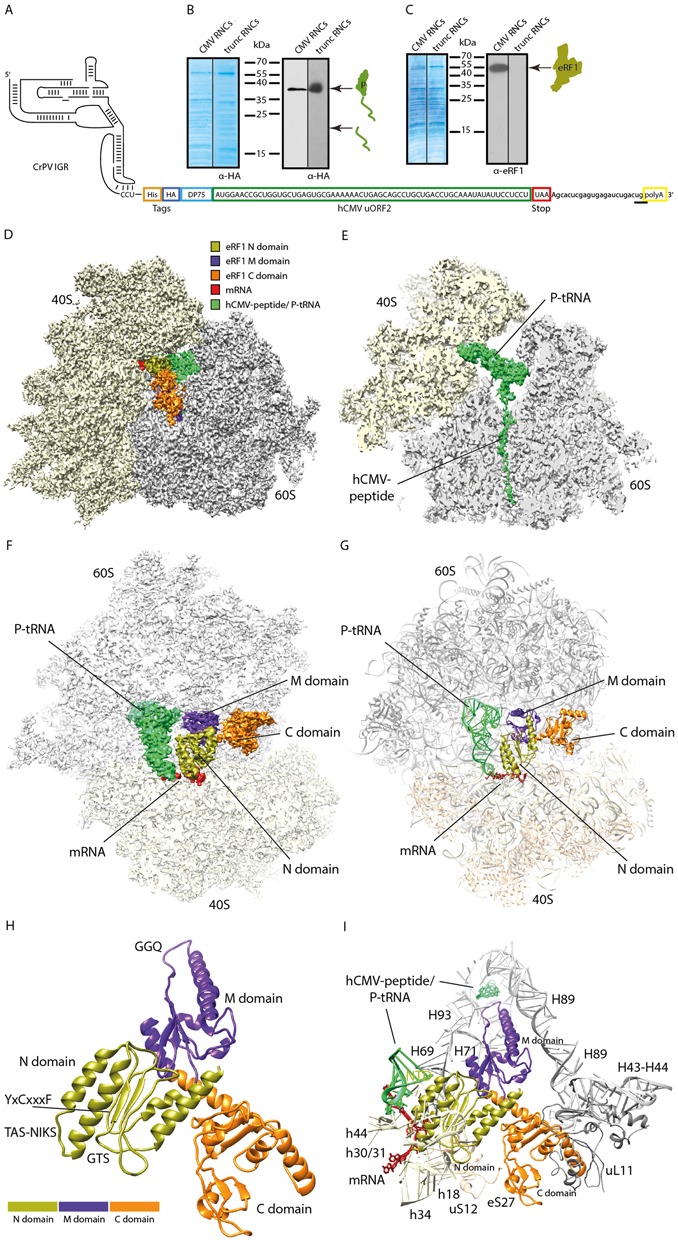
Isolation and cryo-EM structure of a stalled human 80S ribosome bound to eRF1. (A) Schematic representation of the hCMV stalling mRNA construct used in the human translation system for 80S-CMV-RNC generation. The final mRNA construct encoded a CrPV IGR IRES sequence for translation initiation, an N-terminal HA- and (His)6-tag, the well characterized DP75 dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase B (DPAPB) (30), the hCMV uORF2 stalling sequence and a polyA-tail. The termination site relevant for the Stop23Ala mutated construct is underlined. (B, C) Western blots of purified human RNCs programmed with the hCMV mRNA shown in (A) or programmed with truncated mRNA (harbouring no stop codon in the A-site). Signal detection was performed with anti-HA antibody for detection of (B) peptidyl-tRNA or (C) anti-eRF1 antibody. (D) Cryo-EM structure of the eRF1-bound human 80S-CMV-RNC at 3.8 Å resolution. The colour code for mRNA, tRNA and the eRF1 domains is given. (E) Section of (D) focusing on the hCMV peptidyl-tRNA. (F) Top view section of the human eRF1 bound 80S-CMV-RNC cryo-EM structure. (G) Molecular models of (F). For docking, the model of the human ribosome POST structure (pdb code: 5AJ0) and the crystal/NMR structures of human eRF1 (pdb codes: 3E1Y-A, 2KTV) were used. (H, I) Molecular models displaying (H) all 3 eRF1 domains and (I) ribosomal contacts of human eRF1.
