Figure 4.
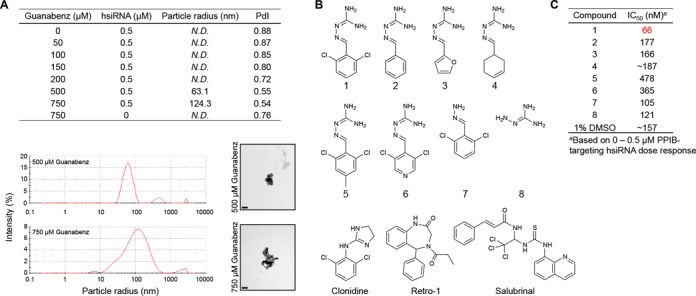
Physicochemical and biological properties of hsiRNA, Guanabenz, and Guanabenz derivatives (A) Characterization of nanoaggregates formed by hsiRNA and Guanabenz. (Top) Size distribution and intensity measured by dynamic light scattering (Nano-ZS, Malvern). N.D. = not detectable; PdI = polydispersity index. (Bottom right) hsiRNA nanoparticle size and morphology examined by transmission electron microscopy following incubation with 500 or 750 μM Guanabenz (Tecnai Spirit 12, FEI, 43,000X). Scale bar = 0.2 μM. (B) Chemical derivatives and/or functional analogs of Guanabenz (1) (C) IC50 values of PPIB-targeting hsiRNA following treatment with Guanabenz and derivatives [100 μM (1–4, 7,8) or 12.5 μM (5,6)] or 1% DMSO. Derivitization results in loss of effect of Guanabenz on hsiRNA IC50.
