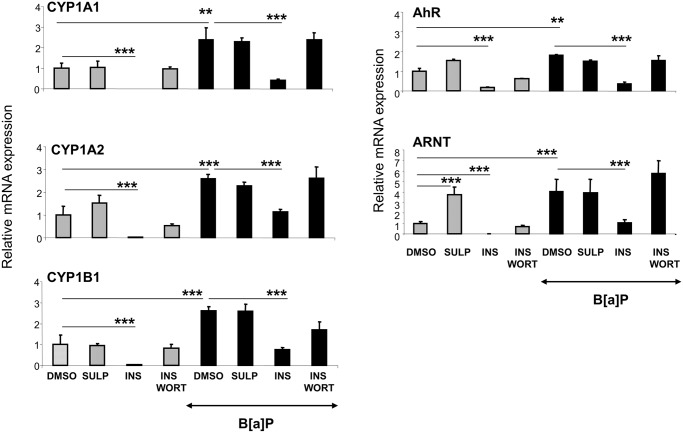
Fig 6. In vitro assessment of the role of dopamine D2-receptor-mediated regulation of hepatic CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and CYP1B1.
Assessments of SULP effects on CYP1A1, CYP1A2 and CYP1B1 relative mRNA expression in primary hepatocytes by using quantitative PCR assays. The role of insulin in the regulation of the above mentioned CYPs was also assessed in primary hepatocyte cultures treated either with insulin (1μM, 24hr) alone or in combination with the inhibitor of the PI3K signalling pathway, wortmannin (1μM, 24hr) [76]. Controls were treated with dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO); SULP: sulpiride (selective dopamine D2-antagonist); INS: insulin; WORT: wortmannin; B[a]P: benzo[a]pyrene; ***P<0.001. Comparisons of the relative CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1, AhR and ARNT mRNA expression between DMSO- and INS-, as well as between DMSO- and (INS+WORT)-treated hepatocytes were done using the Bonferroni’s test and were performed in both, constitutive and B[a]P-induced states. No differences were found between DMSO- and (INS+WORT)-treated hepatocytes, indicating that wortmannin has completely blocked the repressive effect of insulin on both, constitutive and B[a]P-induced mRNA expression of the above mentioned genes.