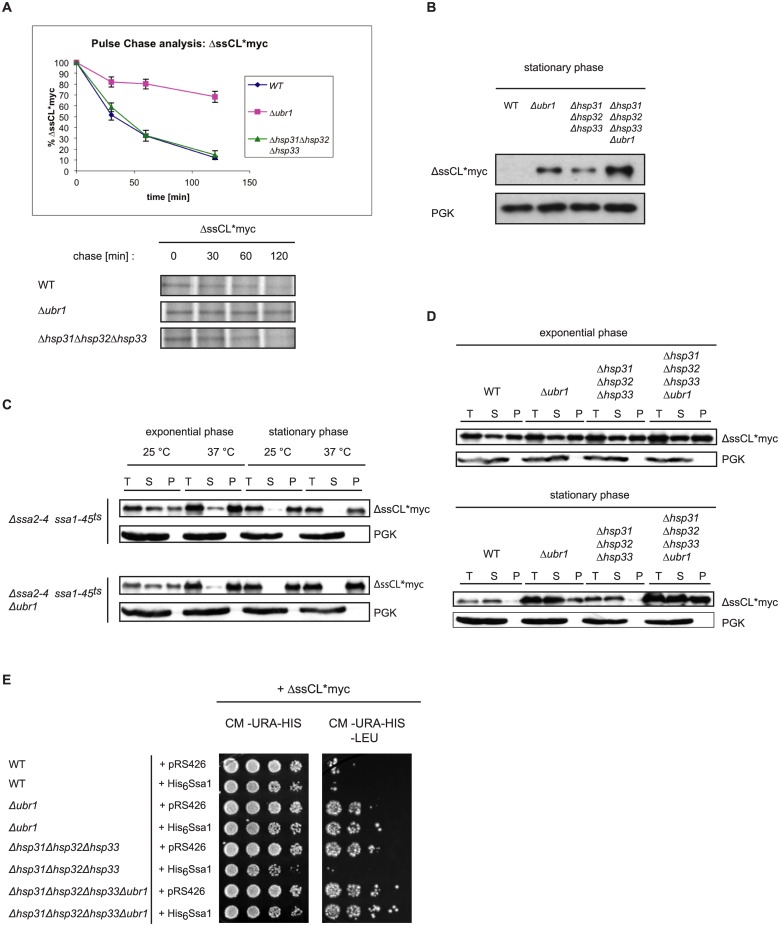
Fig 4. Function of the Hsp31 family in stationary growth phase of cells.
(A) Pulse-chase analysis was done with exponentially-growing yeast cells expressing ΔssCL*myc. Cells were lysed at the indicated time points. Proteins were immunoprecipitated, separated by SDS-PAGE and analysed using a Phosphorimager (Storm 860; Molecular Dynamics) and the ImageQuant software (Amersham Biosciences). Plotted data represent the mean values of three independent experiments. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. (B) Steady state analysis of the amount of the ΔssCL*myc substrate in stationary growth phase. Equal amounts of cells were harvested and cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunodetection using c-Myc antibody. As reference protein, 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) was used. (C) Solubility assays of the misfolded protein ΔssCL*myc expressed in the temperature-sensitive Hsp70 (Ssa) mutant strains Δssa2Δssa3Δssa4ssa1-45 ts and Δssa2Δssa3Δssa4ssa1-45 ts Δubr1. Cells were grown at 25°C before splitting into two halves. One half of the yeast culture was shifted to 37°C for 1 h prior to harvesting, lysis and fractionation into supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions. The total (T) fraction represents the precleared cell lysate. Exponentially growing cells were harvested at an OD600 value of 1.0 whereas stationary cells were grown 3 days prior to temperature shift, cell lysis and fractionation. The different fractions were subjected to TCA precipitation prior to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using c-Myc antibody for substrate detection. PGK served as loading control and reference for a soluble protein. (D) Solubility assays were performed as described for Fig 4C. Strains defective in either Ubr1 or/and the Hsp31 chaperones were used in this assay. The cells were grown at 30°C and harvested either in exponential phase or stationary phase (72h growth), lysed and subjected to fractionation into supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions. The samples were subjected to TCA precipitation, SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using c-Myc antibody. PGK served as loading control and reference for a soluble protein. (E) Growth tests were performed as described earlier. The used strains express the substrate ΔssCL*myc from a HIS3-marker-containing plasmid (pIA1). In addition, the strains were transformed either with the empty plasmid pRS426 containing a URA3 marker or a pRS426-based plasmid expressing functional histidine-tagged Ssa1 under control of the GPD promoter (pAM25).