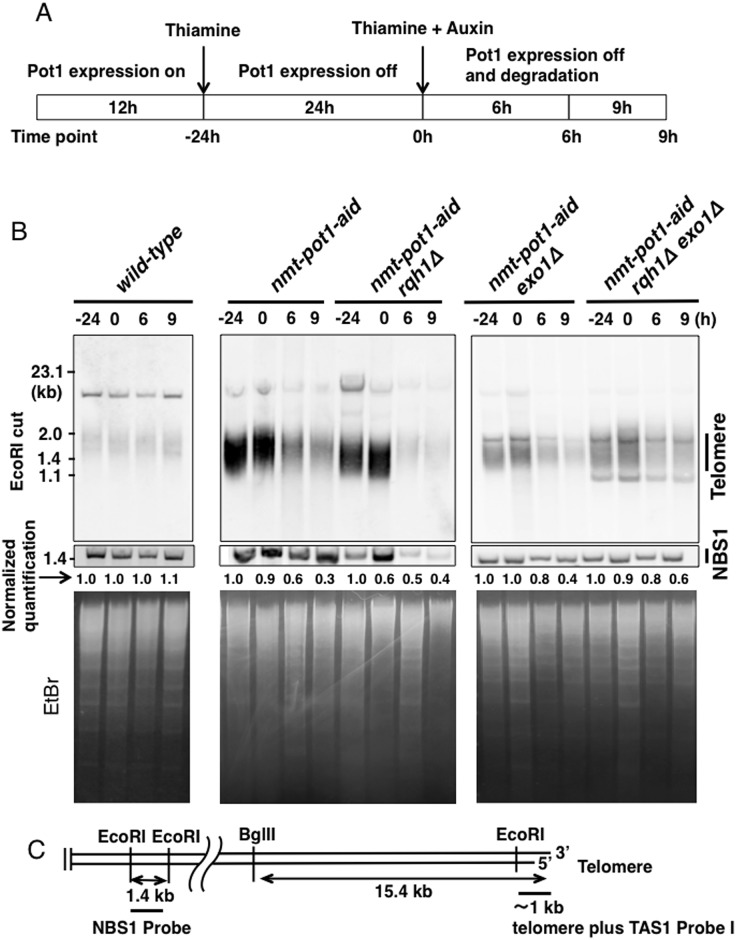
Fig 1. Double deletion of rqh1 + and exo1 + alleviates the telomere loss following Pot1 shut-off.
(A) Experimental design to show how Pot1 function is shut-off. Cells were cultured in EMM medium for 12h without thiamine (time point −24 h). Next, cells were pre-incubated with 15 μM thiamine for 24 h to reduce expression of Pot1 (time point 0 h). Subsequently, both 15 μM thiamine and auxin (0.5 mM of 1-naphtaleneacetic acid) were added and incubated for another 6 h and 9 h (time points: 6 h and 9 h). (B) Telomere length was analyzed using Southern hybridization. Wild-type, nmt-pot1-aid, nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ, nmt-pot1-aid exo1Δ, and nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ exo1Δ strains were used. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI, and resolved by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. A 1-kb DNA fragment containing telomeric DNA plus telomere-associated sequence 1 (TAS1) was used for hybridization (see C). The normalized quantification value of the telomere band is shown below the Southern hybridization data. Image J was used for quantitation. The intensity of the telomere bands was divided by the intensity of the 1.4-kb NBS1 band, located 1.9 Mb from the right telomere in chromosome II, to adjust for loaded DNA fragments (see C). Additionally, in each strain, the band intensity at time point −24 h was normalized to 1. To assess the total amount of DNA, the gel was stained with EtBr, before blotting on to the membrane. (C) Restriction enzyme sites of chromosome ends cloned in the plasmid pNSU70 [42]. The location of the probe used for hybridization is shown by a thick bar. Primers used for amplification of the NBS1 probe are shown in Table 2.