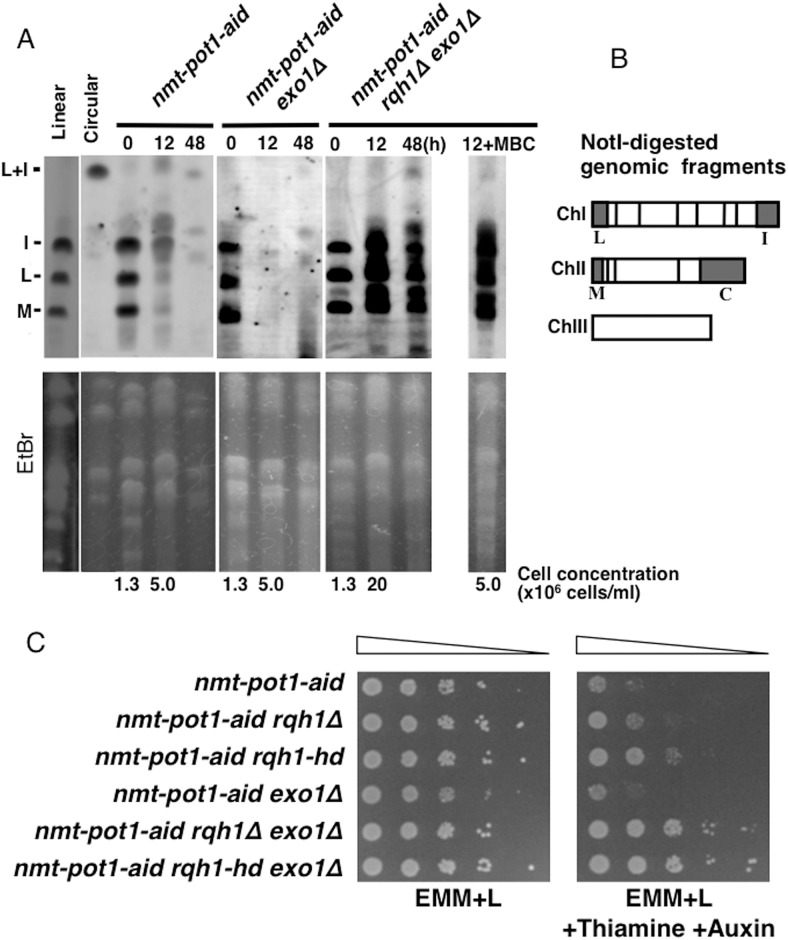
Fig 3. Double deletion of rqh1 + and exo1 + suppresses the loss of NotI-digested chromosome-end fragments and viability following Pot1 shut-off.
(A) The NotI-digested S. pombe chromosomal DNA was analyzed by PFGE. The nmt-pot1-aid, nmt-pot1-aid exo1Δ, and nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ exo1Δ strains were used. Strains with linear (wild-type JY741) and circular chromosomes (pot1Δ KTA045) were used as controls [15]. Cells were incubated as described in Fig 1, except that cells were incubated with thiamine and auxin for 12 h and 48 h. For the nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ exo1Δ strain, 5μg/ml of carbendazim (MBC) was also added at time point 0 h to arrest the cell cycle when indicated (12 h +MBC). Cell concentration at time point 0 h and 12 h is shown below the EtBr data. We used probes specific for the NotI fragments (I, L, and M) [20]. To assess the total amount of DNA, the gel was stained with EtBr before blotting on to the membrane. (B) NotI restriction enzyme map of S. pombe chromosomes, showing chromosomes I, II, and III (ChI, ChII, and ChIII). (C) Spotting assay of a 10-fold serial dilution of cells. We plated nmt-pot1-aid, nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ, nmt-pot1-aid rqh1-hd, nmt-pot1-aid exo1Δ, nmt-pot1-aid rqh1Δ exo1Δ and nmt-pot1-aid rqh1-hd exo1Δ on EMM+L or EMM+L plus thiamine and auxin. Before spotting, cells were pre-incubated with 15 μM thiamine for 24 h to reduce pot1 + expression.