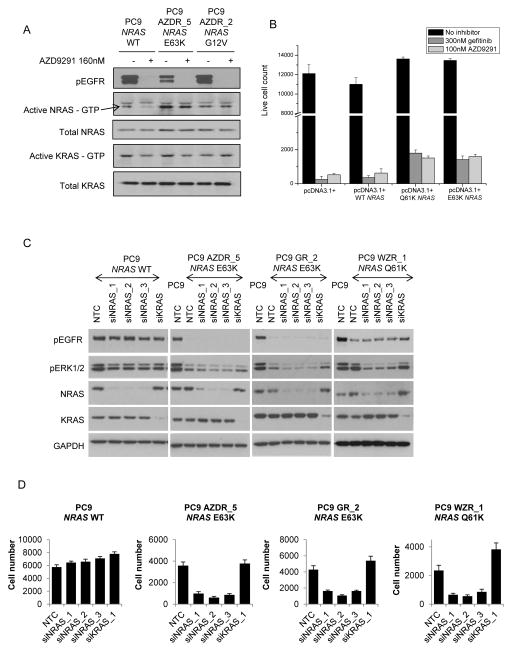
Figure 2. Determining the functional role of NRAS modifications in acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors.
(A) Resistant populations were cultured in media without EGFR inhibitor for 5 days prior to carrying out the assay. Lysates were prepared from parental and resistant cells serum starved overnight and treated for 6 hours +/− 160nM AZD9291. RAS activity was measured using RAS GTPase-specific pulldown assays. (B) PC9 cells transfected with NRAS and control pcDNA 3.1+ constructs for 48 hours were treated with 100nM AZD9291 or 300nM gefitinib for a further 96 hours. Live cell number was determined by nuclei count. The data is representative of three separate experiments. Error bars are standard deviation. (C) Resistant populations were cultured in media supplemented with EGFR inhibitor for all siRNA experiments. Lysates from cells treated with 20nM NTC, NRAS or KRAS siRNA for 48 hours were anlaysed by immunoblotting. (D) Cells treated for 72 hours with 20nM NTC, NRAS or KRAS siRNA were fixed and cell number determined by nuclei count. Data is representative of 3 replicate experiments. Error bars are standard deviation.