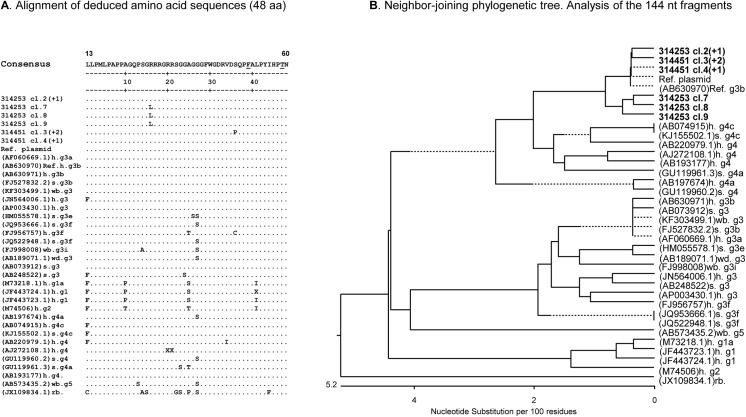
Fig 4. Analysis of the HEV sequences revealed in two sows.
(A) Neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree of nucleotide sequences corresponding to a 144 nucleotides region in ORF2. Sequences from the infected sows #31453 and #314451 are given in bold. After the animal number the number of identical clones derived from the same amplicon is given in brackets as (+n). Accession numbers from the GenBank sequences are indicated. The origin of the sequences is indicated as: h-human; s-swine; wb-wild boar; rb-rabbit. The genotype and subgenotype are given as a number and a small letter, respectively. Absence of the letter means that the subgenotype is unknown. Brackets mark the HEV genotypes 3 and 4 (indicated as gt3 and gt4), respectively. The reference (Ref.) plasmid was designed using WHO standard of HEV (Acc. #AB630970). Nucleotide substitutions per 100 nucleotides are indicated. (B) Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences (48 residues) of cloned HEV sequences from sow #314451 and sow #314253 using Clustal W software. Amino acids substitutions associated with reduced infectivity of HEV (underlined in the consensus sequence) were not detected in the cloned sequences.