FIGURE 1.
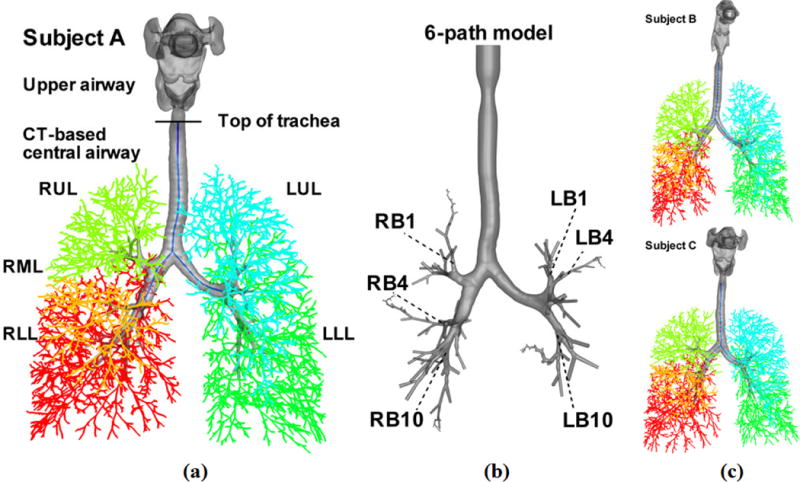
3D and 1D airway geometrical models of subject A in (a), and subject B and subject C in (c). LUL, left upper lobe (blue); LLL, left lower lobes (green); RUL, right upper lobe (light green); RML, right middle lobe (orange); RLL, right lower lobe (red). The CT-based models consist of the upper airways (above the top of trachea) and CT-based central airways (below the top of trachea). (b) The 3D 6 path model of subject A, which consists of the vocal cords, the CT-based central airways and, beyond CT resolution, 6 paths of cylindrical VF airways extending up to the 22nd generation. These 6 paths go through the RB1, RB4, RB10, LB1, LB4, and LB10 segmental bronchi as marked, respectively.4
