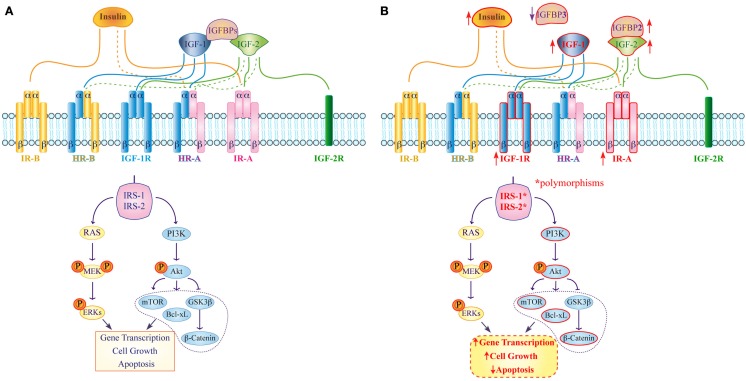
Figure 1.
Expression and function of the insulin/IGF system in normal and colorectal cancer cells. (A) In normal tissue insulin, IGF-1 and IGF-2 bind with high (continuous line) or low (dashed line) affinity to their corresponding receptors and activate specific IRSs, which modulate several pathways involved in gene transcription, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. IGFBPs act as negative regulators that modulate both IGF-1 and IGF-2 functions. (B) In colorectal cancer high IR-A and IGF-1R expression (upward arrow) as well as IRS-1 and IRS-2 polymorphisms are involved in up-regulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway. Moreover, IGFPB3 down-regulation (downward arrow) as well as IGFBP2 overexpression (upward arrow) are involved in strengthening IGF-1 functions and in the activation of intracellular signaling pathways that contribute to alter gene transcription, cellular proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.