Figure 5. The effects of lactate on myometrial Ca2+ signalling .
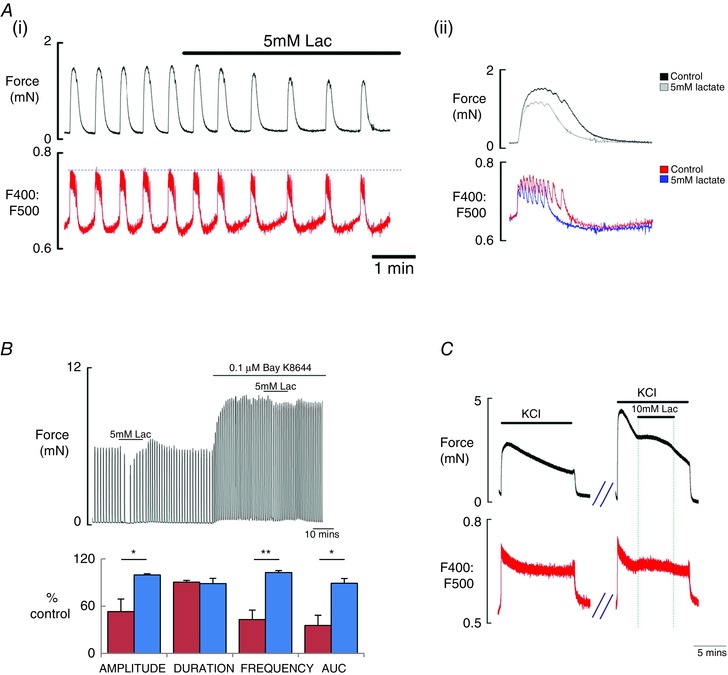
A, simultaneous recording (i) of spontaneous force (top) and Ca2+ (Indo‐1 fluorescence, emission signals at 400 and 500 nm) showing the typical effects of lactate (5 mM) application on rat myometrium; inset (ii) is from the trace and expands and overlaps the force and Ca2+ records during the control period and during lactate application, to show the changes produced by lactate. B, comparison (i) of the effects of lactate using control spontaneous activity and after application of the L‐type Ca2+ agonist, Bay K8644 and (ii) comparing mean data and SEM for effects of lactate on contraction amplitude, duration, frequency and AUC, with and without Bay K8644. C, the effects of high K+ depolarization (40 mM) on force (top) and Ca2+ and the effects of lactate on both.
