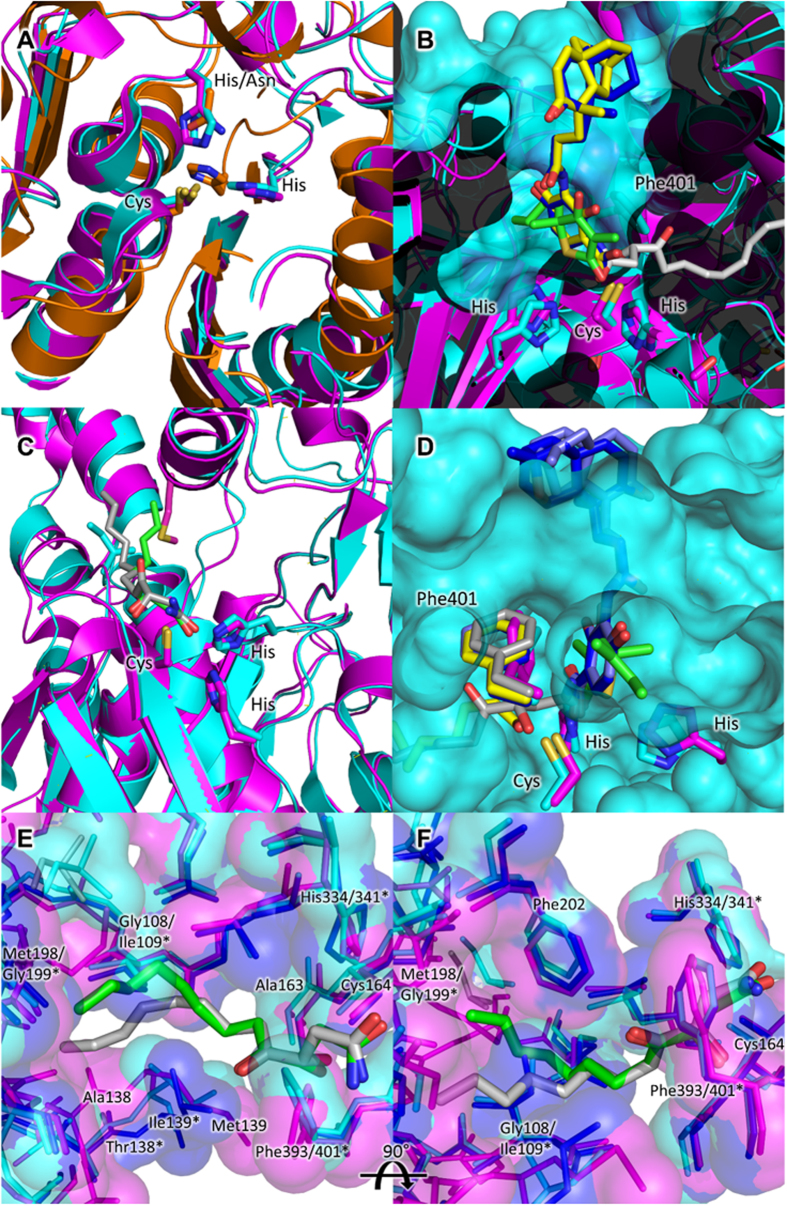
Figure 5. The active sites of Yersinia pestis β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthases and potential interactions with known inhibitors of the FASII condensing enzymes.
(A) Superposition of the putative YpFabH (orange), YpFabF (cyan), and YpFabB (magenta) active sites. (B) Superposition of cerulenin (PDB:1B3N, silver), platencin (PDB:3HO2, yellow), platensimycin (PDB:3HNZ, blue), and thiolactomycin (PDB:1FJ4, green) from bacterial FabF/FabB homologues into the active sites of YpFabB (magenta) and YpFabF (cyan) reveals no steric clashes or modifications which would prevent inhibition, with the exception of Phe401, which is thought to rotate into an open conformation upon substrate or inhibitor binding. (C) Superposition of cerulenin bound E. coli FabB (PDB:1FJ8, silver) and FabF (PDB:1B3N, green) showing the differing conformations of the acyl chain, and residues Ile108 of FabF (cyan) and Met198 of FabB (magenta), which direct the acyl chain of the inhibitor (cyan residue is acting upon green inhibitor, magenta residue is acting upon silver inhibitor) and possibly fatty acyl substrates. (D) A view from the interior of YpFabF, showing access to part of the substrate binding pocket of YpFabF (cyan) is closed off by Phe401. The conformation of Phe401 in FabF/FabB structures bound to cerulenin (PDB:1FJ8, silver), platencin (PDB:3HO2, light blue), platensimycin (PDB 3HNZ, blue), and thiolactomycin (PDB:1FJ4, green) closely mimic that of FabF in complex with lauroyl-CoA (PDB:2GFY, yellow). Superposition of YpFabB (magenta), YpFabF (cyan) and N. meningitidis FabF (PDB:4QAV, dark blue) active sites, and cerulenin from cerulenin bound E. coli FabB (PDB:1FJ8, silver) and FabF (PDB:1B3N, green) structures at 0° (E) and 90° (F) rotation around the vertical axis. Both the residues and surface of the YpFabB and YpFabF active sites and substrate binding pockets are highly similar. The only significant differences appear to be the replacement of Ile109 and Gly199 (Ile108 and Gly199 in E. coli) of FabF, with Gly108 and Met198 of FabB (magenta), and residues 138–140 of both enzymes, with no obvious differences between YpFabF and FabF from N. meningitidis, which does not possess a FabB homologue. YpFabF residues indicated by asterisks (*), YpFabB and residues common to both YpFabB and YpFabF are not marked.