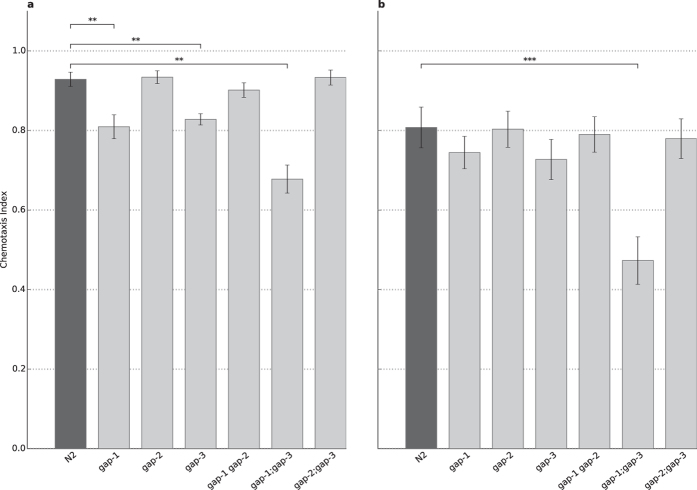
Figure 1. Involvement of various RasGAP isoforms in chemotaxis towards diacetyl.
(A) Chemotaxis to 1:100 diluted diacetyl, attraction of N2 wild type (n = 33) and animals carrying the mutation(s) gap-1(ga133) (n = 9, p = 7.88 × 10−3), gap-2(tm748) (n = 18), gap-3(ga139) (n = 6, p = 2.45 × 10−3), gap-1(ga133) gap-2(tm748) (n = 9), gap-1(ga133);gap-3(ga139) (n = 7, p = 1,80 × 10-3) and gap-2(tm748);gap-3(ga139) (n = 15). (B) Chemotaxis to 1:1000 diluted diacetyl, attraction of N2 wild type (n = 31) and animals carrying the mutation(s) gap-1(ga133) (n = 31), gap-2(tm748) (n = 52), gap-3(ga139) (n = 31), gap-1(ga133) gap-2(tm748) (n = 24), gap-1(ga133);gap-3(ga139) (n = 29, p = 1.17 × 10-14) and gap-2(tm748);gap-3(ga139) (n = 36). Error bars indicate SD and asterisks indicate Bonferroni-corrected significant differences (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).