Figure 6.
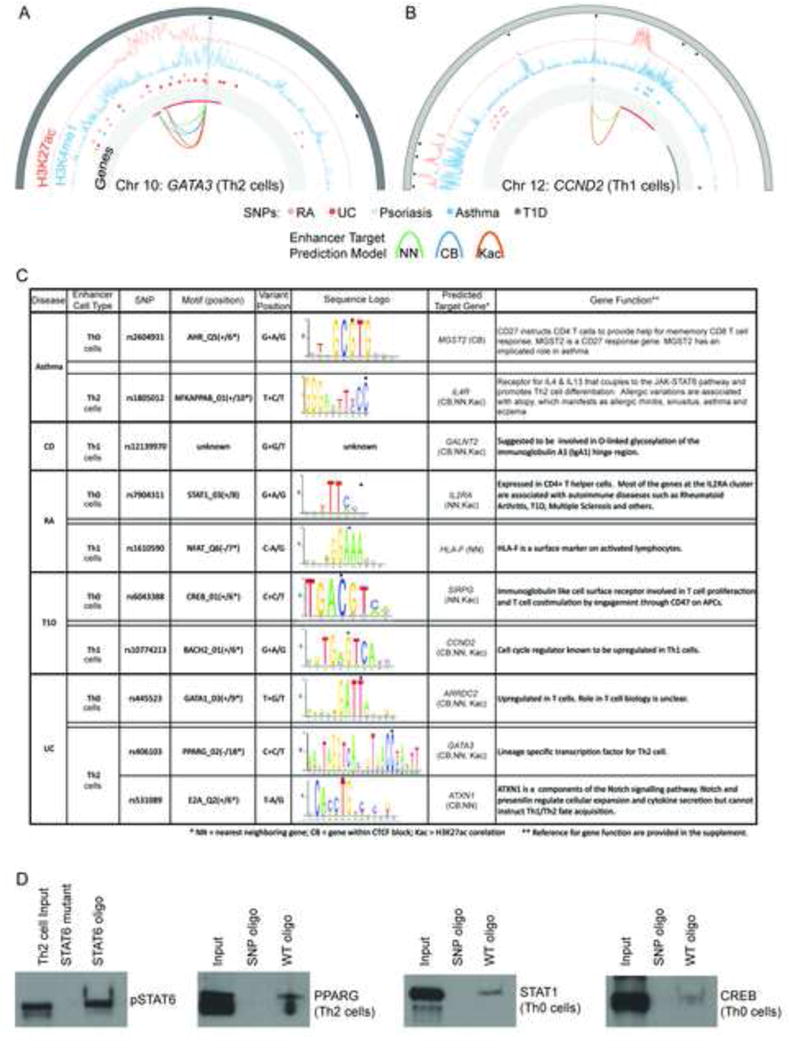
Potential Regulatory Effects of rSNPs at lineage-specific enhancers. (A & B) Circos plots for histone modifications, disease associated SNPs - including rSNPs (open circles), and predicted gene targets at two loci: GATA3 (A) and CCND2 (B). The outermost track shows the chromosome bands. Black boxes note enriched H3K4me1 peaks. Lineage-specific enhancers are displayed with light grey radial lines. The profiles show H3K27ac (orange) and H3K4me1 (blue). Disease SNPs are shown with color-coded circle as indicated. The SNPs overlapping a lineage-specific enhancer are highlighted as empty circles. Innermost track (with light grey background) shows the genes (upregulated in red, rest are grey). Arcs connect enhancers to genes based on the target prediction method (green: NN, blue: CB, orange: KAc). (C) List of a subset of SNPs associated with RA, T1D, Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Asthma that lie directly within known motifs of TFs (dot over base), that play and important role in T cell biology. Crohn’s disease (CD) rSNPs did not overlap with any known motifs. Predicted target genes of the effected enhancers are listed to further elucidate the potential effect of the SNP. References for gene function are given in supplement. (D) DAPA (DNA Affinity Precipitation Assay) experiments to determine if disease associated rSNPs can alter transcription factor binding to their predicted binding sites at enhancers. Double-stranded oligonucleotides containing the predicted PPARG, STAT1, and CREB binding sites at enhancers were used as bait. Binding was assayed using nuclear extracts from activated (Th0 cell) or polarised T cells (Th1, Th2 cells) at 72 h as indicated. The oligonucleotide bait containing the SNPs at transcription factor binding sites are shown in 6C (see Supplemental Materials and methods for complete probe sequences). DNA sequence with STAT6 binding site and a negative control DNA sequence (oligonucleotide where STAT6 binding site has been mutated) are provided as controls for DAPA. TF binding to oligonucleotides was detected by western blotting using antibodies specific to the selected transcription factors (See Supplemental Methods for antibodies used). Data shown is representative for three biological replicates (See Figure S5).
