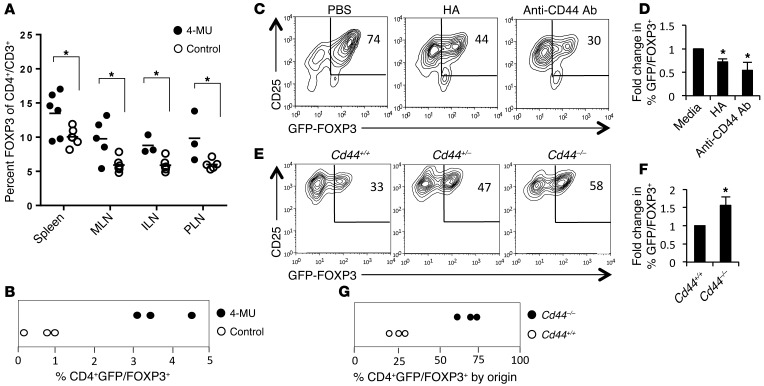
Figure 8. 4-MU treatment relieves CD44-mediated inhibition of FOXP3 induction.
(A) Percentage of GFP/FOXP3+ Tregs of total CD4+ T cells in BALB/c mice fed 4-MU or control chow for 2 weeks (n = 5–6 mice per group). (B) In vivo induction of FOXP3+ Tregs assessed 4 days after transfer of GFP/FOXP3–CD4+ T cells into Rag–/– hosts given 4-MU or control chow (n = 3 Rag–/– recipient animals). Data are from the spleens of recipient animals. (C) CD25 and FOXP3 expression by CD4+GFP/FOXP3– T cells activated for 72 hours with or without plate-bound HA or anti-CD44 antibody. (D) Pooled data for 3 independent experimental replicates for the representative data in C. (E) FOXP3 induction using Cd44+/+, Cd44–/+, or Cd44–/– precursors. (F) Pooled data for 3 independent experimental replicates for the representative data in E. (G) In vivo induction of FOXP3 assessed using cotransfer of equivalent numbers of GFP/FOXP3–CD4+Cd44+/+CD45.1 and GFP/FOXP3–CD4+Cd44–/–CD45.2 T cells into Rag–/– hosts. After 4 days, the numbers of induced CD3+GFP/FOXP3+ Tregs in the spleens of recipient animals were assessed and the ratio of Cd44–/– Tregs versus Cd44+/+ Tregs was determined (n = 3 Rag–/– recipient animals). Data represent mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05 vs. respective control by unpaired t test.