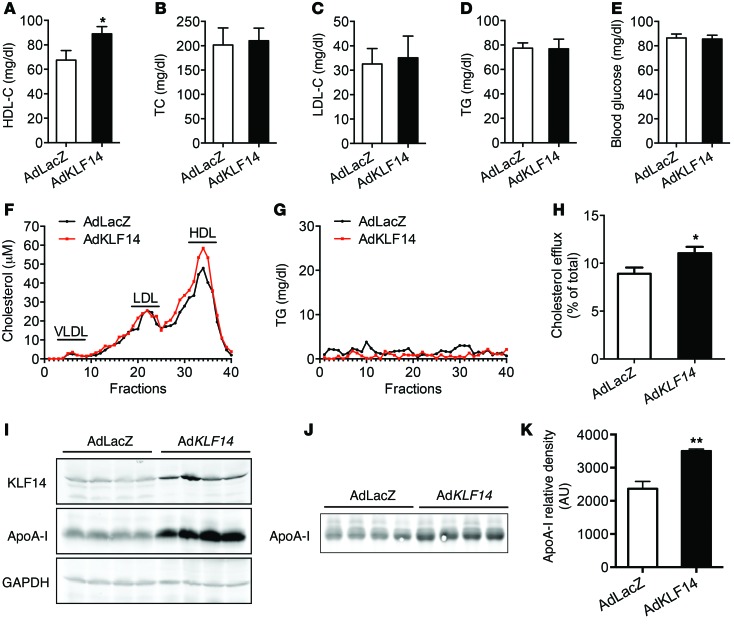
Figure 1. Overexpression of KLF14 increases both HDL-C and ApoA-I levels and cholesterol efflux capacity.
Adenoviral vectors containing LacZ (AdLacZ) or human KLF14 (AdKLF14) (5 × 108 pfu per mouse) were administered via tail vein injection to C57BL/6 mice fed HFD for 12 weeks (n = 10 per group). Serum samples were collected at day 6 and subjected individually to analytical chemistry to measure HDL-C (A), TC (B), LDL-C (C), TG (D), and fasting blood glucose (E) or to determine cholesterol and TG levels from pooled samples by FPLC (fractions 1 to 40) (F and G). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. (H) The ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity of serum from AdKLF14- or AdLacZ-treated mice is expressed as the percentage of cholesterol efflux of total cell cholesterol (n = 10 per group). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. Representative Western blot results show that AdKLF14-treated mice exhibited increased expression of ApoA-I levels in the liver (I) and serum (J). (K) Quantifications of ApoA-I levels in the serum from AdLacZ and AdKLF14-treated mice by Western blot (n = 10 per group). Values represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, Student’s t test.