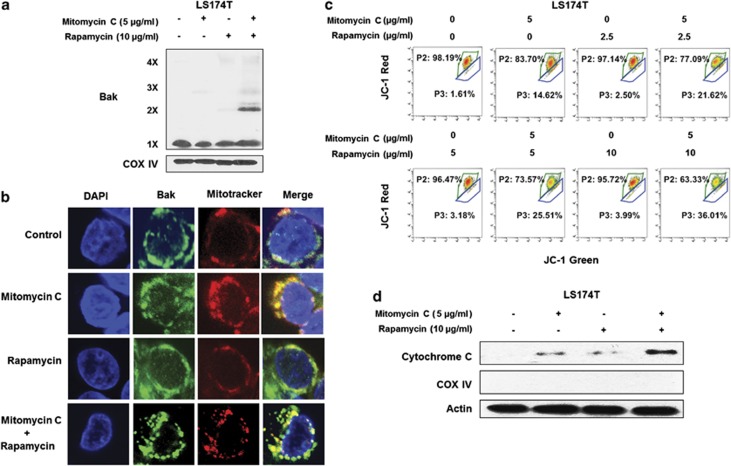
Figure 4.
The combination of mitomycin C and rapamycin induced Bak oligomerization and mitochondria dysfunction. (a) LS174T cells were treated with mitomycin C (5 μg/ml) and/or rapamycin (10 μg/ml) for 24 h. After treatment, mitochondria were isolated, cross-linked with 1 mM dithiobis (succinimidyl propionate) and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Bak antibody. Bak monomer (1X) and multimers (2X, 3X, and 4X) are indicated. COX IV was used as a mitochondrial marker. (b) LS174T cells were treated with mitomycin C (2 μg/ml) and/or rapamycin (5 μg/ml) for 24 h. After treatment, mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker. Bak was stained with anti-Bak antibody. Localization of Bak was examined by confocal microscopy. (c) LS174T cells were treated with mitomycin C (5 μg/ml) and/or rapamycin (10 μg/ml) for 24 h. After treatment, cells were stained with JC-1 and analyzed by flow cytometry. (d) Cytochrome c release into cytosol was determined by immunoblotting for cytochrome c in the cytosolic fraction. Actin was used to confirm the equal amount of proteins loaded in each lane