Figure 1. BuGZ promotes spindle assembly independent of kinetochores.
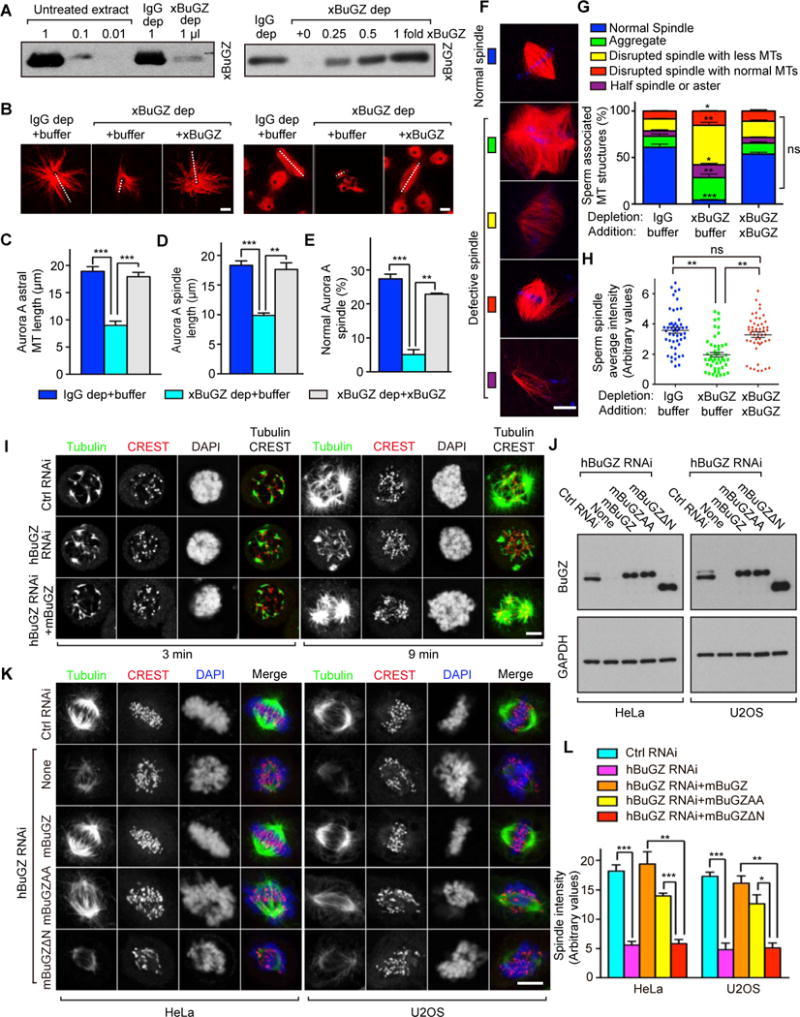
A. Western blotting of xBuGZ depletion (left) and add-back (right) in extracts. xBuGZ depletion (dep) efficiency and xBuGZ addition are shown in titrations.
B–E. Representative images (B) show that xBuGZ depletion reduced astral MT length, bipolar spindle formation and length, which were all rescued by His-xBuGZ. ~50 (C, D) or ~500 (E) structures were measured in each experiment and condition. White dashed lines in B indicate Aurora A spindle length and longest astral MTs measured.
F–H. xBuGZ depletion caused multiple sperm spindle defects (F), which was rescued by His-xBuGZ (G, H). ~500 (G) and ~50 (H) structures were analyzed in each experiment and condition.
I. hBuGZ depletion reduced astral MT re-growth in mitotic HeLa cells, and was rescued by mBuGZ. Cold-treated cells were examined at 3 or 9 min after returning to 37°C. MTs, centromeres, and chromosomes were stained by tubulin antibody, CREST serum, and DAPI, respectively.
J. Western blotting analyses of HeLa and U2OS cells treated by hBuGZ siRNA and transfected with indicated plasmids.
K–L. HeLa or U2OS images (K) show that hBuGZ depletion by 72 h of RNAi diminished MT intensity in spindles, and was rescued fully by mBuGZ, partially by mBuGZAA, but not by mBuGZΔN. Cells were blocked with 10 μM MG132 for 1 h before immunostaining. ~30 cells were measured for each experiment and condition (L). Error bars, standard error of the means (SEM). Student’s t-test: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, three independent experiments. Scale bars, 5 μm.
