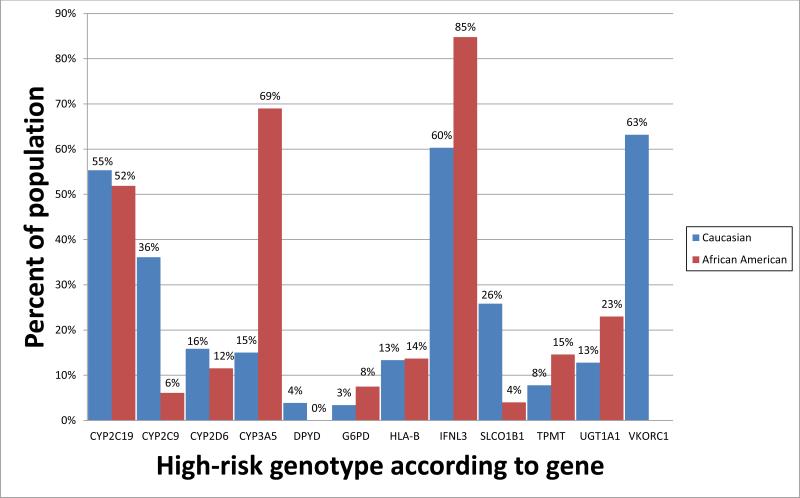
Figure 1.
Percentage of individuals expected to have a high-risk diplotype for 12 genes identified by the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) to have at least one known actionable inherited variant plotted by self-reported race category [white (red bars) or black (blue bars)]. For the genes CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A5, SLCO1B1, TPMT, UGT1A1, and VKORC1, diplotype frequencies were obtained from the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital PG4KDS study, based on data from 624 black patients and 732 white patients. Due to small sample size in other race categories, other race categories were omitted from the figure. For the genes for which validated diplotype data were not yet available from the PG4KDS study, (DPYD, G6PD, HLA-B, and IFNL3), high-risk diplotype frequencies were estimated using published allele frequency data (7; 8; 13; 15; 48).
High risk diplotypes were considered as follows: for CYP2C19, diplotypes containing a *2 , *3 or *17 allele; for CYP2C9, diplotypes containing a *2 or *3 allele; for CYP2D6, diplotypes resulting in activity scores of < 1 or > 2; for CYP3A5, diplotypes containing a *1 allele; for DPYD, diplotypes containing *2A, *3, or the rs67376798 A variant; for G6PD, those with G6PD deficient phenotypes; for HLA-B, diplotypes containing a *5701 or *5801 allele; for IFNL3, diplotypes containing an rs12979860 T allele; for SLCO1B1, diplotypes containing a *5 or *15 allele; for TPMT, diplotypes containing a *2, *3A, *3B, *3C, *4 or *8 allele; for UGT1A1, diplotypes containing two copies of the *28 allele; and for VKORC1, diplotypes containing an rs9923231 A allele. High-risk diplotypes for blacks were not calculated for VKORC1 due to the low predictive value of genotype-driven warfarin dosing in this population.