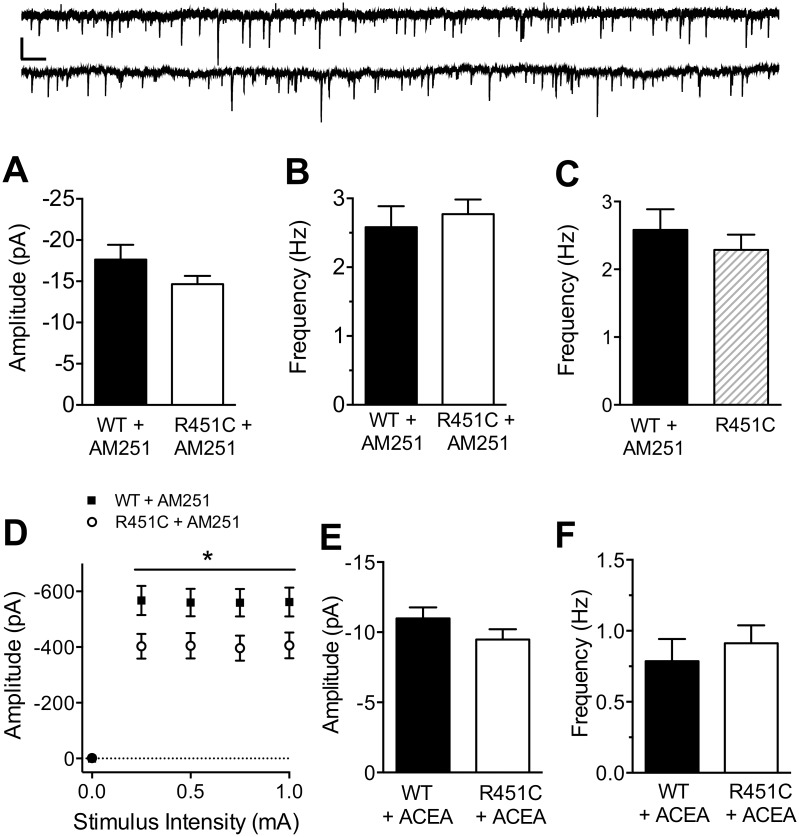
Fig 6. Tonic endocannabinoid signaling is decreased at cortical inhibitory synapses in Nlgn3R451C mice.
Mean amplitude (A) and frequency (B) of mIPSCs recorded in the presence of 1 μM TTX and 10 μM AM 251 from pyramidal neurons of WT (n = 23) and Nlgn3R451C (n = 23) mice. Inset: 15 s raw traces from WT (top) and Nlgn3R451C (bottom) pyramidal neurons. Scale bar = 25 pA, 0.5 s. C) The Nlgn3R451C-mediated increase in mIPSC frequency is occluded by bath application of AM 251 to neurons from WT mice (WT + AM 251 = 23, Nlgn3R451C = 32). D) Input/output curves recorded in the presence of 10 μM AM 251 using the same range of stimulus intensities as in Fig 1C (WT = 22, Nlgn3R451C = 23). Mean Amplitude (E) and frequency (F) of mIPSCs recorded in the presence of CB1 receptor agonist ACEA (10 μM; WT = 24, Nlgn3R451C = 25).* P < 0.05.