Figure 1.
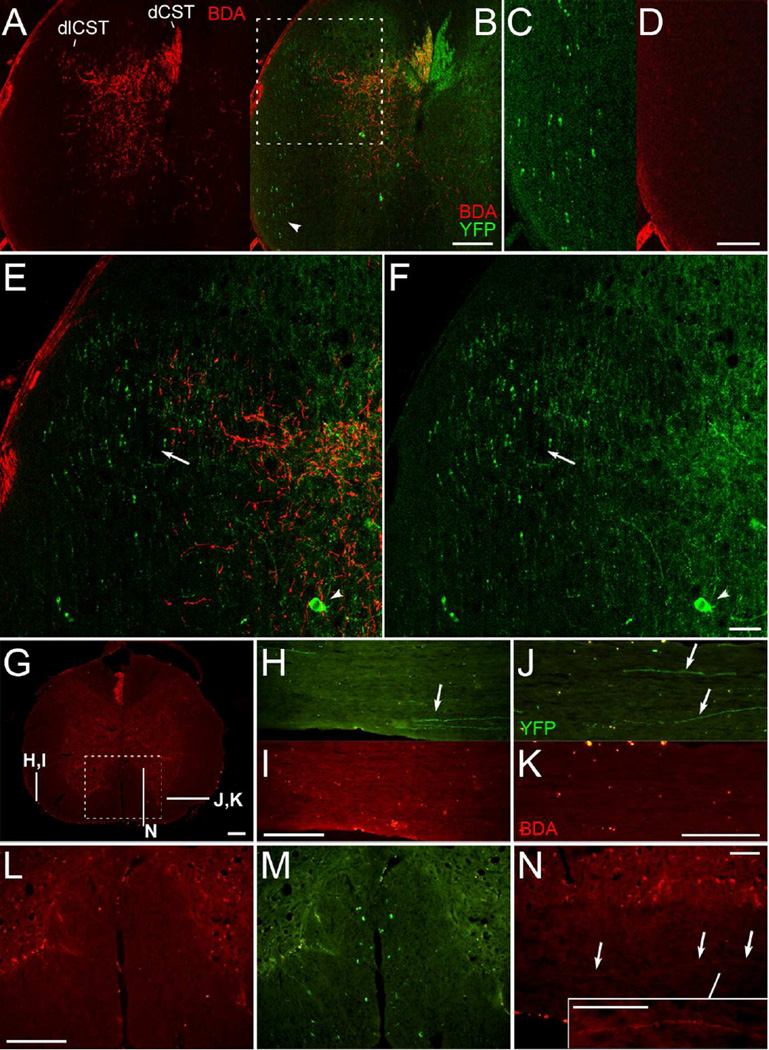
YFP-labeled axons are in areas of the spinal cord that do not contain anterogradely-labeled CST axons. A-F, Confocal images of a spinal cord cross section with amplified BDA signal. BDA labeled CST axons (A) are illustrated relative to YFP labeling (B) following BDA injections into the right sensorimotor cortex. The ventral lateral white matter (arrowhead, B) is enlarged in C and D; note the absence of BDA-labeled axons in D. The dorsolateral column (boxed region in B) is shown in higher magnification in E-F; arrowheads indicate YFP-labeled neurons in the grey matter; arrows indicate the region of the rubrospinal tract, which overlaps with the dlCST. Note that some YFP-labeled axons in this region are distinctly thicker in appearance. G, Cross section with mini-ruby BDA labeling and indicated locations of sections shown in H-N. H-K, Sections in ventral lateral white matter with YFP-labeled axons (arrows in H-J) and as shown for BDA labeling (I,K); note the bilateral absence of BDA-labeled axons. L-M, BDA (L) and YFP labeling (M) in the ventral column (boxed region from G). N, A BDA-labeled axon coursing longitudinally in the ventral column ipsilateral to the injected cortex, as seen in one of 14 mice. The inset in N has been further enhanced for contrast. This figure with magenta-green confocal panels is available as Supplementary Figure S1. dCST, dorsal corticospinal tract; dlCST, dorsolateral CST. Scale bars, 200 µm (A-B, G-M), 100 µm (C-D, N and inset), 50 µm (E-F).