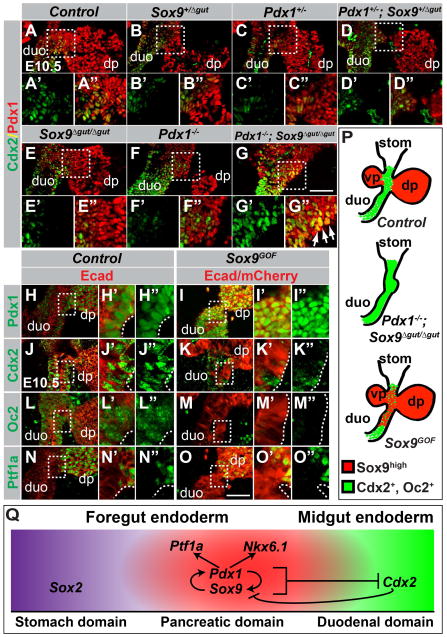
Figure 6. Pdx1 and Sox9 are necessary and sufficient to repress the intestinal lineage choice.
(A–G) Immunofluorescence analysis for Pdx1 and Cdx2 on E10.5 embryos carrying various combinations of Pdx1 and Sox9 mutant alleles. In compound Pdx1;Sox9 heterozygous mutant or Pdx1 or Sox9 single-homozygous mutant embryos, Cdx2 expression is restricted to duodenal precursors and excluded from the Pdx1high dorsal pancreas (A–F). In Pdx1−/−;Sox9Δgut/Δgut embryos, a duodenal-pancreatic junction is not discernable and Pdx1 and Cdx2 are co-expressed in a broad domain (arrows in G″). (H–O) Immunofluorescence staining of sections from Sox9GOF and control littermates shows repression of the intestinal markers Cdx2 (J,K) and Onecut-2 (Oc2; L,M) in mCherry+ duodenal precursors in Sox9GOF mice. Pdx1 is upregulated (H,I) but Ptf1a is not induced (N,O) in duodenal precursors in Sox9GOF embryos. Fields demarcated by dashed boxes in A–O are shown at higher magnification in A′–O″. (P) Summary of the phenotypes observed after combined Pdx1 and Sox9 deletion or Sox9 overexpression. (Q) Graphical model summary. Our data support a model whereby Pdx1 and Sox9 cooperatively specify the pancreatic lineage by inducing the pancreatic transcription factors Nkx6.1 and Ptf1a and repressing the duodenal transcription factor Cdx2. A positive regulatory loop between Pdx1 and Sox9 maintains the pancreatic fate choice. Repression of Sox9 by Cdx2 creates bistability of the fate choice (Gao et al. 2009). dp, dorsal pancreatic bud; vp, ventral pancreatic bud; duo, duodenum; stom, stomach. Scale bar = 50 μm.