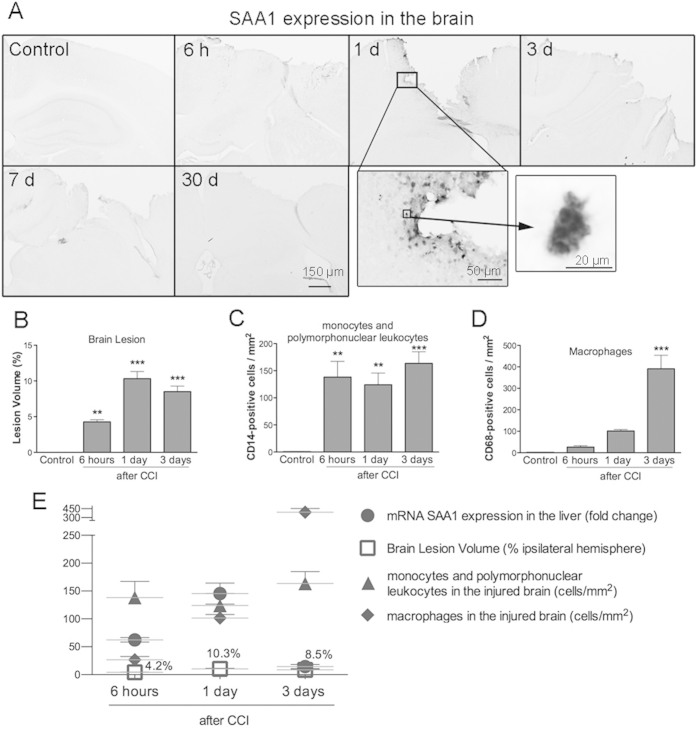
Supplemental Figure S1.
Acute inflammatory response in the brain, cortical lesion, and serum amyloid A1 (SAA1) expression in the liver. A: Immunohistochemical images showing SAA1 expression in the brain in naïve control mice and at 6 hours and 1, 3, 7, and 30 days after injury. Sparse SAA1-positive cells are observed near the border of the lesion, with vacuolated morphology (high-magnification images) at 1 day post-injury (dpi). B: Cortical lesion volume was measured and was greatest at 1 and 3 dpi. C and D: The number of monocytes or polymorphonuclear leukocytes (CD14-positive cells); C) dramatically increases at 6 hours post-injury (hpi) and is maintained up to 3 dpi; however, the number of macrophages (CD68-positive cells) reaches a peak at 3 dpi (D) in the cortical region bordering the impact site. E: Relationship between hepatic SAA1 expression, inflammatory cell density in the brain, and brain lesion volume at 6 hpi and 1 and 3 dpi. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (B–D). n = 5 to 8 per group (B–D). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, comparing injured brains with control brains. CCI, cortical impact injury.