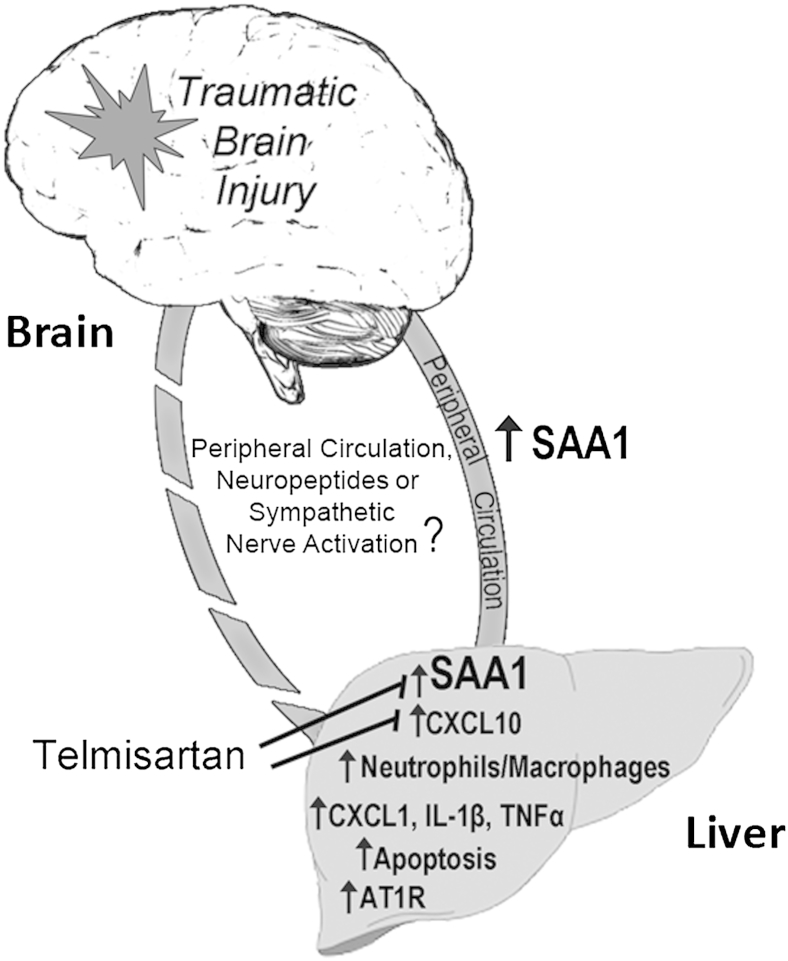
Figure 6.
Interplay of liver inflammation induced by traumatic brain injury. The bidirectional interactions between the injured brain and peripheral tissues, including liver, are controlled by cytokines in the peripheral circulation, neuropeptides, or sympathetic nerve activation. After traumatic brain injury, hepatic inflammation is indicated by higher expression of serum amyloid A1 (SAA1) and proinflammatory cytokines, infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages, and the presence of apoptotic cells. Telmisartan reduces SAA1 and CXCL10 expression. AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.