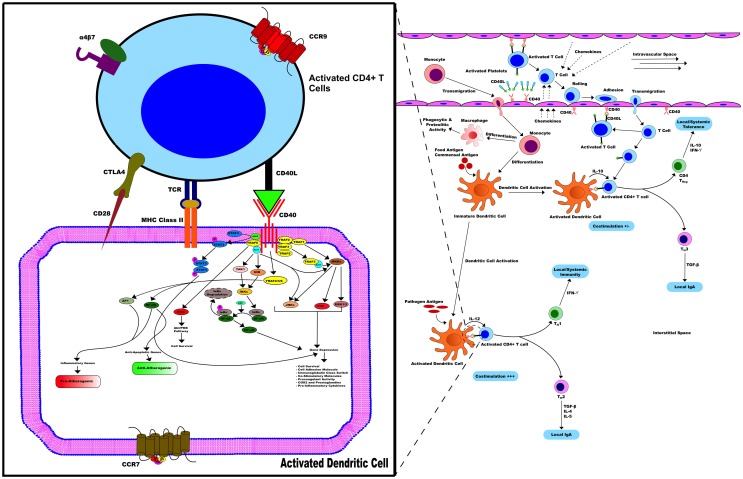
Figure 2.
CD40/CD40L in IBD. CD40/CD40L axis contributes to the activation of various pathways related to inflammation in immune and non-immune cells, hence promoting IBD. In the early stages of mucosal inflammation, local T cells become activated and express CD40L, binding to and activating CD40+ DC. Therefore, CD40+ DC enhances cytokine secretion, such as IL-12, and up-regulation of co-stimulatory activity including CD40, CD40L, and MHC-II activity promoting more T cells that transmigrate into the interstitial space become activated with expressed CD40L. Activated T cells in the circulation of patients with IBD contribute to this process through expression of CD40L on their surface.