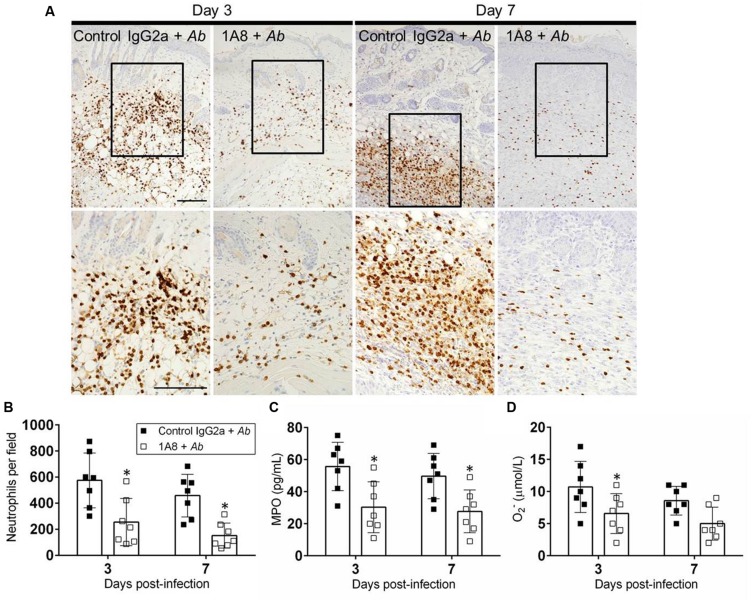
FIGURE 5.
MAb 1A8 administration decreases cutaneous neutrophil infiltration. (A) IHC of MPO released by neutrophils in wounds removed from A. baumannii-infected (control IgG2a + A. baumannii), and mAb 1A8-treated A. baumannii-infected (1A8 + A. baumannii) mice. MPO-specific mAb was used to stain MPO (dark) released in skin tissue indicative of neutrophil infiltration. Inset shows restricted dermal accumulation of neutrophils. Representative 20X (upper panel) and 40X (lower panel; magnified black boxes in upper panel) MPO-immunostained sections of the skin lesions are shown. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) Number of neutrophils per field in wounded skin tissue of control IgG2a + A. baumannii and 1A8 + A. baumannii animals. (C) MPO concentration in the supernatant of tissue homogenates excised from control IgG2a- and mAb 1A8-treated A. baumannii-infected mice. (D) Superoxide (O2-) production was quantified by measurement of SOD1 activity in tissue homogenates excised from control IgG2a + A. baumannii and 1A8 + A. baumannii mice. For (B–D), bars represent the mean values for seven clinical isolates (each symbol); error bars denote standard deviations. Asterisks denote P-value significance (∗P < 0.05) calculated using student’s t-test analysis. The experiments were performed twice with similar results obtained.