Figure 4.
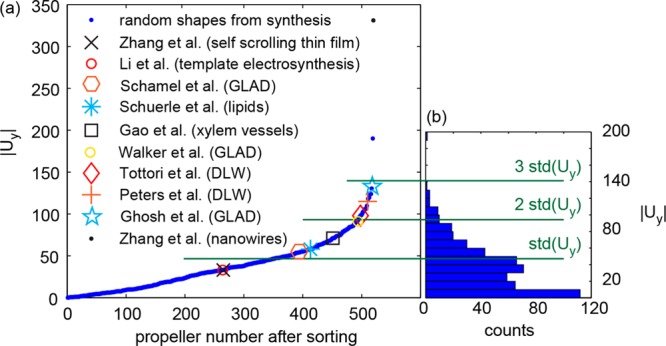
Comparison of randomly shaped propellers from solution synthesis with previously published nanofabricated propellers. The dimensionless speeds of nanofabricated propellers are shown in increasing order as in Supporting Information Figure S3 (Zhang et al.,11 Li et al.,35 Schamel et al.,18 Schuerle et al.,33 Gao et al.,34 Walker et al.,22 Tottori et al.,23 Peters et al.,32 Ghosh et al.,17 Zhang et al.16). (a) The absolute value of dimensionless speeds of the random shapes and the dimensionless speed values from the literature are assigned a propeller number, by sorting the values in ascending order. The dimensionless speed of both random shapes and nanofabricated propellers is then plotted against the propeller number. The propeller number of a nanofabricated propeller is thus an indication of how many random shapes (from the set of the 512) have a lower dimensionless speed. (b) The distribution of absolute dimensionless speed values is displayed as a histogram. The scale of |Uy| is the same as in (a). The multiples of the standard deviation of Uy are displayed as horizontal green lines. Assuming a Gaussian distribution, 68% of random shapes have dimensionless speeds lower than the one standard deviation, 95% lower than two, and 99.7% lower than three standard deviations.
