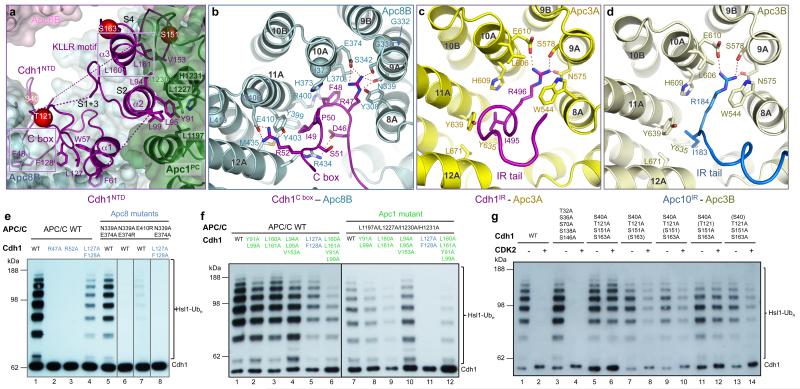
Figure 2. The C box of Cdh1 and IR tails of Cdh1 and Apc10 interact with structurally related sites on Apc8 and Apc3.
(a) Cdh1NTD binds to Apc8 and Apc1. Segments 1 and 3 of Cdh1NTD including the C box interact with Apc8, whereas segments 2 and 4 interact with Apc1PC. Segments 1-4 are labelled as S1-4. Phosphorylation sites S40, S151 and S163 as red spheres. (b) Details of the C box-interactions. The R47 and I49 interaction sites are structurally related to the IR tail-binding sites for Cdh1 and Apc10 in Apc3 shown in (c, d). S. cerevisiae CDC23 (Apc8) temperature-sensitive mutations 23 map to the C box-binding site (Cα of mutant residues shown as spheres in (b)). (e) Mutation of C box-residues Arg47 and Arg52 eliminates APC/CCdh1 activity, as do mutation of Apc8 residues that interact with either Arg47 or Arg52. (f) At the Cdh1NTD – Apc1PC interface multiple residues cooperate to mediate APC/C – Cdh1 interactions. (g) S40, S151 and S163 mediate the negative regulation of Cdh1 by CDK phosphorylation.