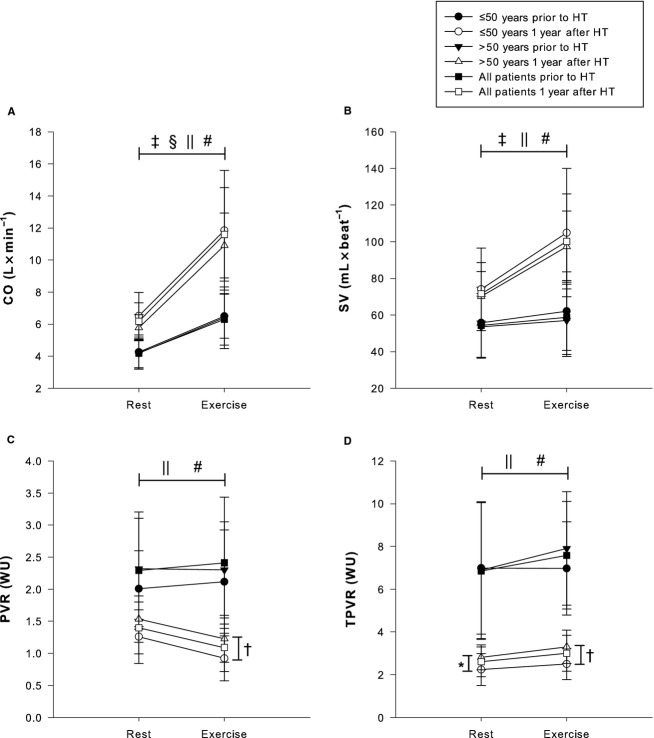
Figure 3.
Hemodynamic response to exercise with regard to cardiac output, stroke volume, and pulmonary vascular resistances prior to and 1 year after HT. • Patients aged ≤50 years prior to HT. ○ Patients aged ≤50 years 1 year after HT. ▾ Patients aged >50 years prior to HT. Δ Patients aged >50 years 1 year after HT. ▪ All 32 patients prior to HT. □ All 32 patients 1 year after HT. A, CO. B, SV. C, PVR. D, TPVR. *A statistically significant difference for TPVR at rest between patients aged ≤50 and >50 years 1 year after HT. †A statistically significant difference for PVR and TPVR during exercise between patients aged ≤50 and >50 years. ‡A statistically significant difference for CO and SV between rest and exercise prior to HT for patients aged ≤50 years. §A statistically significant difference for CO between rest and exercise prior to HT for patients aged >50 years. ‖A statistically significant difference for CO, SV, PVR, and TPVR between rest and exercise at 1 year after HT for patients aged ≤50 years. #A statistically significant difference for CO, SV, PVR, and TPVR between rest and exercise at 1 year after HT for patients aged >50 years. CO indicates cardiac output; HT, heart transplantation; PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance; SV, stroke volume; TPVR, total pulmonary vascular resistance; WU, Wood units.