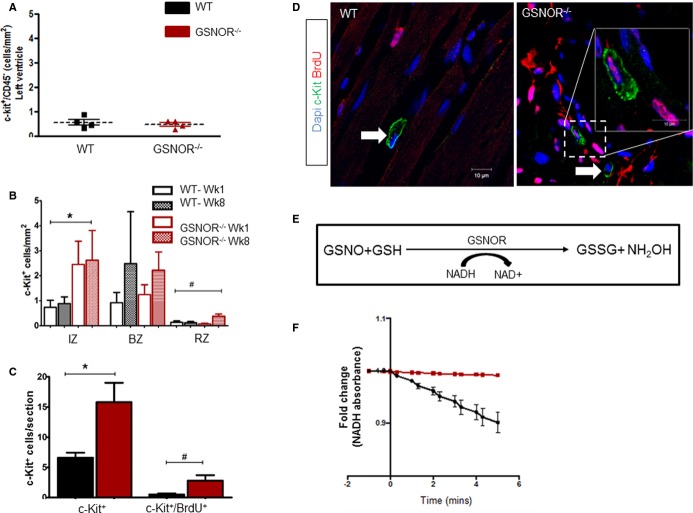
Figure 4.
Enhanced proliferative expansion of c-Kit+ CSCs in GSNOR−⁄− hearts post MI. A, At baseline, healthy adult WT and GSNOR−⁄− mice have an equivalent number of c-Kit+ CSCs (t test; P=0.5942). B, c-Kit+ CSC at 1 and 8 weeks post MI in the infarct, border and remote zones of WT and GSNOR−⁄− mice (2-way ANOVA; *P=0.013 between WT and GSNOR−⁄−; #P=0.03 within groups). C, One month after MI,GSNOR−⁄− mice have significantly more c-Kit+ CSCs in their hearts, compared with WT. In addition, significantly more c-Kit+ CSCs have incorporated BrdU in GSNOR−⁄− mice compared with WT, suggesting that GSNOR−⁄− c-Kit+ CSCs have an enhanced proliferative capacity after MI (Mann–Whitney test; *P=0.0016 and #P=0.012). D, Representative confocal photomicrographs of BrdU incorporation by cardiac c-Kit+ CSCs in WT and GSNOR−⁄− hearts, 1 month post MI. Two GSNOR−⁄− c-Kit+ CSCs are shown, one of which has incorporated BrdU (inset) whereas the other has not (arrow). E, Principle of the GSNOR activity assay. GSNOR catalyzes the reduction of GSNO to GSSG in the presence of NADH. Thus, the activity of GSNOR can be indirectly estimated, by spectrophotometrically monitoring NADH oxidation. F, GSNOR enzymatic activity in c-Kit+ CSCs. GSNOR activity is enriched in WT, but is absent in GSNOR−⁄− progenitors. Data are presented as individual data (A) or mean±SEM (B and C) or fold-change (E); WT (n=6) GSNOR−⁄− (n=5). *P=0.01 and #P=0.02. ANOVA indicates analysis of variance; BrdU, 5-bromodeoxyuridine; BZ, border zone; CSC, cardiac stem cell; GSNOR, S-nitrosoglutathione reductase; GSSG, glutathione disulfide (oxidized GSH); IZ, infarct zone; MI, myocardial infarction; NADH, reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD); RZ, remote zone; WT, wild-type.