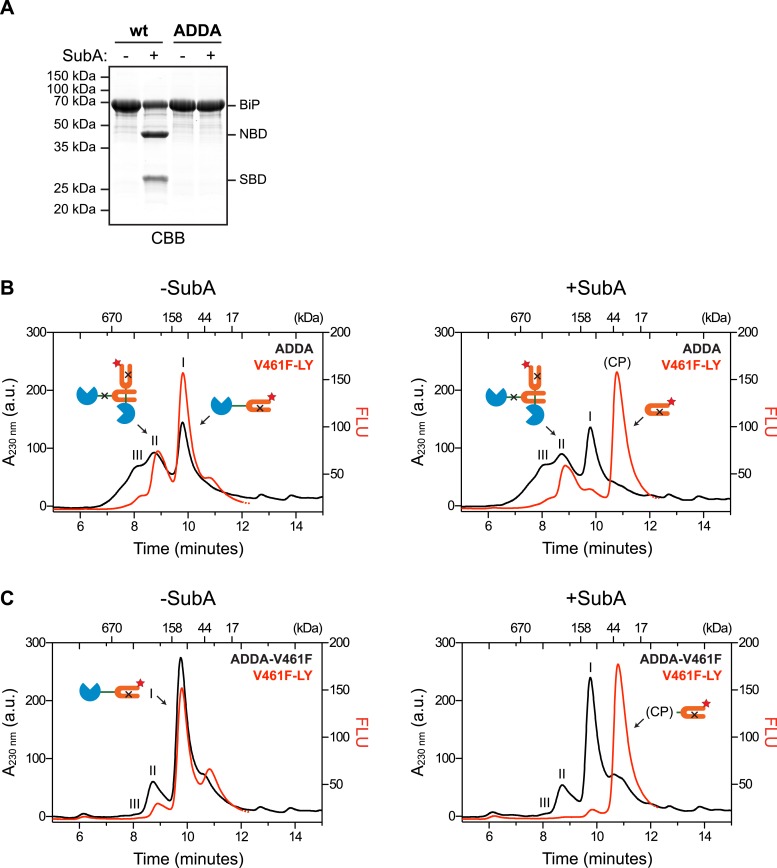
Figure 3. Cross-protomer engagement of the interdomain linker in BiP oligomers protects it against cleavage by SubA.
(A) Coomassie-stained SDS-gel of wildtype (wt) and ADDA mutant BiP (12 µM) before and after cleavage with SubA (0.25 ng/µl) for 15 min. Note that the ADDA mutation precludes cleavage by SubA. (B) Peptide bond absorbance trace (A230 nm, black) and fluorescence trace (in arbitrary fluorescence units, FLU) of lucifer yellow (LY) (Ex: 430 nm, Em: 525 nm; red) of purified ADDA mutant BiP (50 µM) incubated with tracer concentrations (1 µM) of lucifer yellow-labeled V461F mutant BiP (V461F-LY) and fractionated by size-exclusion chromatography (as in Figure 2) either before (-SubA) or after (+SubA) cleavage with SubA (36 ng/µl). Peaks I, II and III are marked as is the new fluorescent peak emanating from the V461F-LY cleavage product (CP). Note that fluorescent peak I, corresponding to the V461F mutant BiP monomer is attenuated after cleavage with SubA, whereas peak II, arising from hetero-oligomers of ADDA mutant BiP and V461F mutant BiP is relatively resistant. The peptide-bond absorbance trace (A230 nm), contributed largely by the ADDA mutant BiP, is unchanged by cleavage with SubA. (C) Experiment as in ‘B’ with purified double mutant ADDA-V461F BiP (50 µM) and lucifer yellow-labeled V461F mutant BiP (V461F-LY). Note the absence of a SubA-resistant fluorescent peak II in this sample.