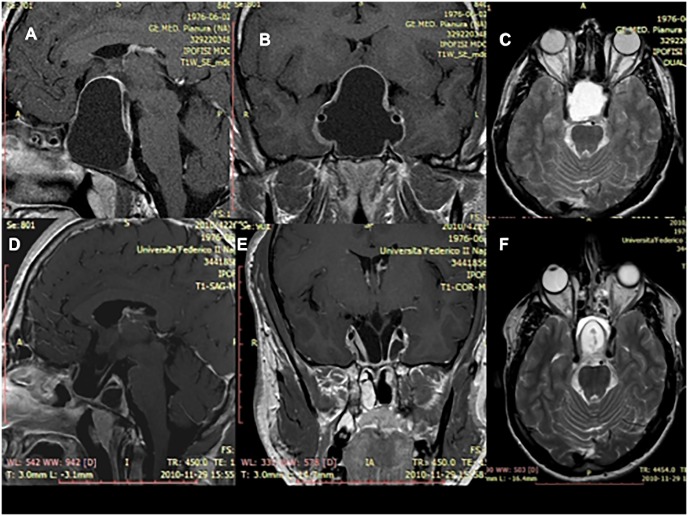
Fig 2. MRI scan after gadolinium showing an intra and suprasellar Rathke’s Cleft Cyst before and after the surgical removal via a standard endoscopic endonasal approach (case showed in the Fig 1).
(A-B) Sagittal and a coronal T1-weighted scans of the lesion before being removed. The colloid has a hypointense signal and the cyst wall has post contrast enhancement. These features do not define typical aspect of RCC, whose differential diagnosis with sellar arachnoid cysts could be often challenging. (C) Axial T2-weighted scan of the lesion showing the colloid with a hyperintense signal. (D-E) Sagittal and a coronal T1-weighted scans and (F) axial T2-weightedscan at the three months postoperative MRI showing the cyst removal. It is possible to identify the decompression of the optic chiasm and the pituitary stalk.