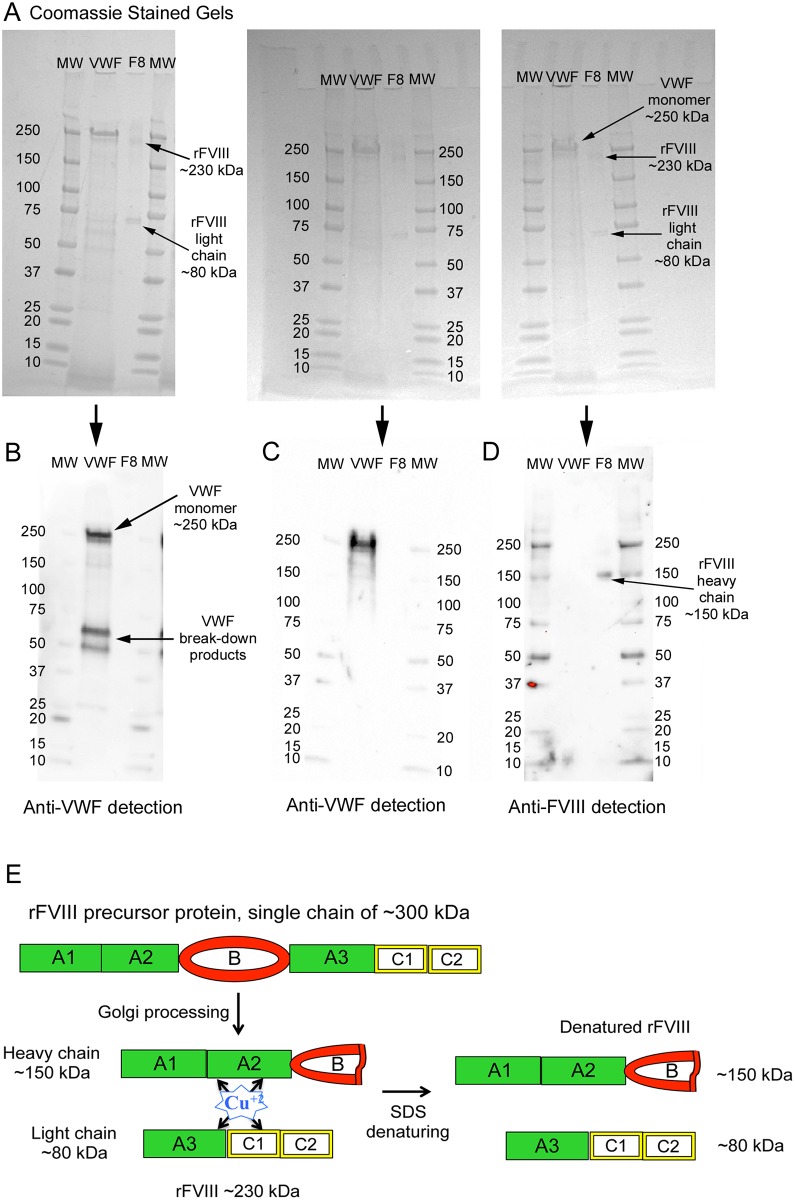
Fig 1. Specificity of antibodies to human FVIII and VWF.
Denatured, non-reduced samples of recombinant (r) FVIII [Helixate FS, 130 ng per lane (1.30 IU)] and denatured, reduced samples of plasma purified VWF (90–130 ng per lane) were separated by 4–15% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-PAGE. Lanes containing rFVIII are marked as F8 and MW indicates molecular weight markers in kDa. (A) Arrows on the Coomassie stained gels show the ~230 and ~80 kDa bands for rFVIII and the monomer subunit of reduced VWF at ~250 kDa. (B, C and D) Western blots of gels shown in (A) were detected in (B) with goat anti-human VWF plus donkey anti-goat-HRP, in (C) with rabbit anti-human VWF plus donkey anti-rabbit-HRP, and in (D) with mouse monoclonal anti-human FVIII plus goat anti-mouse-HRP. Panel (E) is a schematic drawing illustrating the interpretation of the Coomassie stained bands and anti-FVIII detected bands generated from denatured rFVIII. The addition of SDS to rFVIII results in the dissociation of copper (Cu) ions [30,31] (or other ions that may be involved, such as the calcium and manganese ions required for FVIII activation) that bridge the heavy chain (~150 kDa) and light chain (~80 kDa) of the rFVIII protein (~230 kDa). [1] The rFVIII was produced using a ~90 kDa B domain. (The B domain was cleaved within the Golgi of the producing BHK cells prior to processing and metal coordination, resulting in a heavy chain of ~150 kDa.) [29].